ST08: Eco-Approach and Departure at Signalized Intersections
The Eco-Approach and Departure at Signalized Intersections service package uses wireless data communications sent from a connected vehicle roadside equipment (RSE) unit to connected vehicles to encourage 'green' approaches to and departures from signalized intersections. The vehicle collects intersection geometry information and signal phase movement information using V2I communications and data from nearby vehicles using V2V communications. Upon receiving this information, the service package performs calculations to provide speed advice to the driver, allowing the driver to adapt the vehicle's speed to pass the next traffic signal on green or to decelerate to a stop in the most eco-friendly manner. The service package also considers a vehicle's acceleration as it departs from a signalized intersection.
Relevant Regions: Australia, Canada, European Union, and United States
- Enterprise
- Functional
- Physical
- Goals and Objectives
- Needs and Requirements
- Sources
- Security
- Standards
- System Requirements
- Implementations
Enterprise
Development Stage Roles and Relationships
Installation Stage Roles and Relationships
Operations and Maintenance Stage Roles and Relationships
(hide)
| Source | Destination | Role/Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Maintains |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Manager | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Manages |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Vehicle Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Supplier | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Driver | Vehicle | Operates |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | ITS Roadway Equipment | Maintains |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | ITS Roadway Equipment | Manages |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Supplier | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Other Vehicles Maintainer | Other Vehicles | Maintains |
| Other Vehicles Manager | Other Vehicles | Manages |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Driver | Vehicle Operating Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Other Vehicles Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Other Vehicles Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Vehicle Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Supplier | Other Vehicles Owner | Warranty |
| Traffic Management Center Maintainer | Traffic Management Center | Maintains |
| Traffic Management Center Manager | Traffic Management Center | Manages |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Traffic Management Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Traffic Management Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transportation Information Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Supplier | Traffic Management Center Owner | Warranty |
| Transportation Information Center Maintainer | Transportation Information Center | Maintains |
| Transportation Information Center Manager | Transportation Information Center | Manages |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Vehicle Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Supplier | Transportation Information Center Owner | Warranty |
| Vehicle Maintainer | Vehicle | Maintains |
| Vehicle Manager | Driver | System Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Manager | Vehicle | Manages |
| Vehicle Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Vehicle Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Other Vehicles Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Other Vehicles Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Vehicle Owner | Other Vehicles User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Vehicle Supplier | Vehicle Owner | Warranty |
Functional
This service package includes the following Functional View PSpecs:
Physical
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG.SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
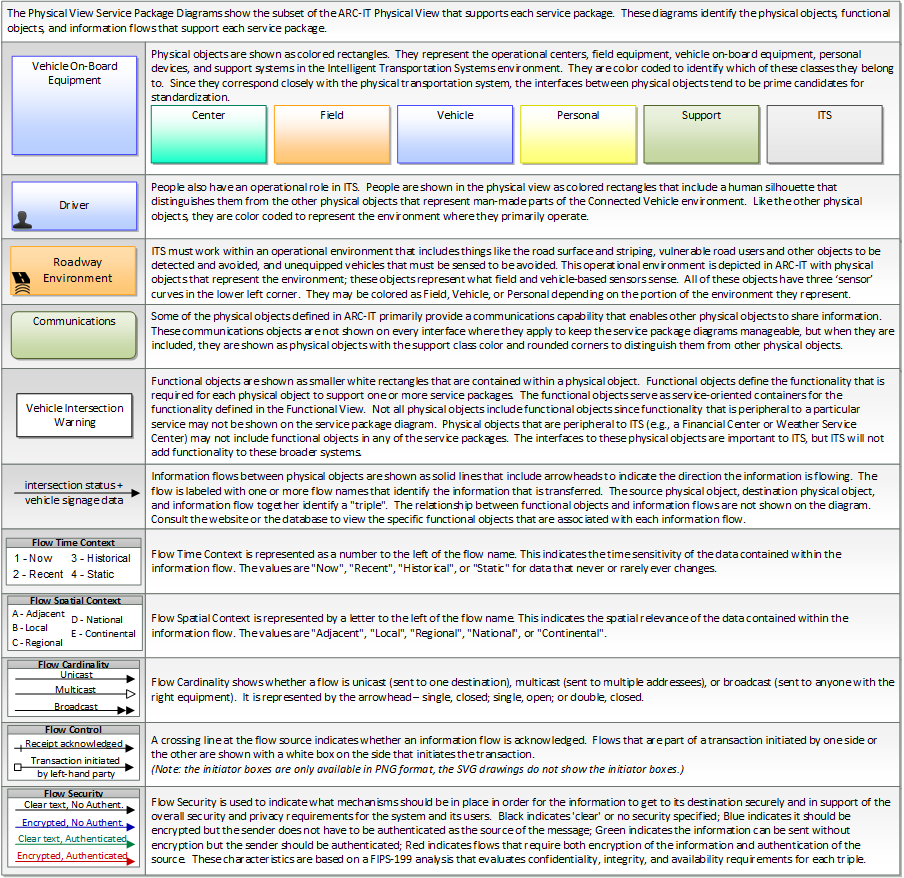
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment' (CV RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices (i.e., Roadside Units (RSUs)) equipped with short range wireless (SRW) communications technology, as well as any other supporting equipment that leverage the RSU and are not described by other objects (e.g., a local roadside processor). CVRSE are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles and personal devices equipped with compatible communications technology. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway. This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | 'Other Vehicle OBEs' represents other connected vehicles that are communicating with the host vehicle. This includes all connected motorized vehicles including passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles and specialty vehicles (e.g., maintenance vehicles, transit vehicles) that also include the basic 'Vehicle OBE' functionality that supports V2V communications. This object provides a source and destination for information transfers between connected vehicles. The host vehicle on-board equipment, represented by the Vehicle OBE physical object, sends information to, and receives information from the Other Vehicle OBEs to model all connected vehicle V2V communications in ARC-IT. |
| Traffic Management Center | Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Transportation Information Center | Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
| Vehicle | Vehicle | This 'Vehicle' physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to more than one type of Vehicle. It provides the vehicle-based general sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions that support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. Many of these capabilities (e.g., see the Vehicle Safety service packages) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle. Both one-way and two-way communications options support a spectrum of information services from basic broadcast to advanced personalized information services. Advanced sensors, processors, enhanced driver interfaces, and actuators complement the driver information services so that, in addition to making informed mode and route selections, the driver travels these routes in a safer and more consistent manner. This physical object supports all six levels of driving automation as defined in SAE J3016. Initial collision avoidance functions provide 'vigilant co-pilot' driver warning capabilities. More advanced functions assume limited control of the vehicle to maintain lane position and safe headways. In the most advanced implementations, this Physical Object supports full automation of all aspects of the driving task, aided by communications with other vehicles in the vicinity and in coordination with supporting infrastructure subsystems. |
Includes Functional Objects:
| Functional Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Roadway Signal Control | 'Roadway Signal Control' includes the field elements that monitor and control signalized intersections. It includes the traffic signal controllers, detectors, conflict monitors, signal heads, and other ancillary equipment that supports traffic signal control. It also includes field masters, and equipment that supports communications with a central monitoring and/or control system, as applicable. The communications link supports upload and download of signal timings and other parameters and reporting of current intersection status. It represents the field equipment used in all levels of traffic signal control from basic actuated systems that operate on fixed timing plans through adaptive systems. It also supports all signalized intersection configurations, including those that accommodate pedestrians. In advanced, future implementations, environmental data may be monitored and used to support dilemma zone processing and other aspects of signal control that are sensitive to local environmental conditions. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Intersection Management | 'RSE Intersection Management' uses short range communications to support connected vehicle applications that manage signalized intersections. It communicates with approaching vehicles and ITS infrastructure (e.g., the traffic signal controller) to enhance traffic signal operations. Coordination with the ITS infrastructure also supports conflict monitoring to ensure the RSE output and traffic signal control output are consistent and degrade in a fail safe manner. | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring | 'RSE Traffic Monitoring' monitors the basic safety messages that are shared between connected vehicles and distills this data into traffic flow measures that can be used to manage the network in combination with or in lieu of traffic data collected by infrastructure-based sensors. As connected vehicle penetration rates increase, the measures provided by this application can expand beyond vehicle speeds that are directly reported by vehicles to include estimated volume, occupancy, and other measures. This object also supports incident detection by monitoring for changes in speed and vehicle control events that indicate a potential incident. | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment |
| TIC Traffic Control Dissemination | 'TIC Traffic Control Dissemination' disseminates intersection status, lane control information, special vehicle alerts, and other traffic control related information that is real-time or near real-time in nature and relevant to vehicles in a relatively local area on the road network. It collects traffic control information from Traffic Management and other Center(s) and disseminates the relevant information to vehicles and other mobile devices. | Transportation Information Center |
| TMC Signal Control | 'TMC Signal Control' provides the capability for traffic managers to monitor and manage the traffic flow at signalized intersections. This capability includes analyzing and reducing the collected data from traffic surveillance equipment and developing and implementing control plans for signalized intersections. Control plans may be developed and implemented that coordinate signals at many intersections under the domain of a single Traffic Management Center and are responsive to traffic conditions and adapt to support incidents, preemption and priority requests, pedestrian crossing calls, etc. | Traffic Management Center |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication | 'Vehicle Basic Safety Communication' exchanges current vehicle characteristics, location, and motion (including past and intended maneuver) information with other vehicles in the vicinity, uses that information to calculate vehicle paths, and warns the driver when the potential for an impending collision is detected. If available, map data is used to filter and interpret the relative location and motion of vehicles in the vicinity. Information from on-board sensors (e.g., radars and image processing) are also used, if available, in combination with the V2V communications to detect non-equipped vehicles and corroborate connected vehicle data. This object represents a broad range of implementations ranging from basic Vehicle Awareness Devices that only broadcast vehicle location and motion and provide no driver warnings to advanced integrated safety systems that coordinate maneuvers and may, in addition to warning the driver, provide collision warning information to support automated control functions that can support control intervention. | Vehicle |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist | 'Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist' provides customized real-time driving advice to drivers, allowing them to adjust behaviors to save fuel and reduce emissions. This advice includes recommended driving speeds, optimal acceleration and deceleration profiles based on prevailing traffic conditions, and local interactions with nearby vehicles, i.e., processing Basic Safety Messages (BSMs) to determine position and speed of vehicles that are between the host vehicle and the intersection. When approaching and departing signalized intersections, it uses intersection geometry information, the relative position and speed of vehicles ahead of it, and signal phase movement information to provide speed advice to the driver so that the driver can adapt the vehicle's speed to pass the next traffic signal on green, decelerate to a stop in the most eco-friendly manner, or manage acceleration as the vehicle departs from a signalized intersection. It also provides feedback to drivers on their driving behavior to encourage them to drive in a more environmentally efficient manner. It may also support vehicle-assisted strategies, where the vehicle automatically implements the eco-driving strategy (e.g., changes gears, switches power sources, or reduces its speed in an eco-friendly manner as the vehicle approaches a traffic signal or queue). | Vehicle |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| conflict monitor status | A control flow that supports failsafe operation in the event that a conflict is detected that requires the RSE to enter a failsafe operating mode for intersection management. Analogous to a traffic signal conflict monitor, this flow is issued when differences are detected between information provided to the vehicle for in-vehicle display and information displayed by field devices. It contains the details of differences that were found. |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information provided to the driver to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. |
| intersection control status | Status data provided by the traffic signal controller including phase information, alarm status, and priority/preempt status. |
| intersection geometry | The physical geometry of an intersection covering the location and width of each approaching lane, egress lane, and valid paths between approaches and egresses. This flow also defines the location of stop lines, cross walks, specific traffic law restrictions for the intersection (e.g., turning movement restrictions), and other elements that support calculation of a safe and legal vehicle path through the intersection. |
| intersection management application info | Intersection and device configuration data, including intersection geometry, and warning parameters and thresholds. This flow also supports remote control of the application so the application can be taken offline, reset, or restarted. |
| intersection management application status | Infrastructure application status reported by the RSE. This includes current operational state and status of the RSE and a log of operations. |
| intersection status | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow identifies active lanes and lanes that are being stopped and specifies the length of time that the current state will persist for each lane. It also identifies signal priority and preemption status and pedestrian crossing status information where applicable. |
| intersection status monitoring | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow represents monitoring of communications by a receiver at the intersection to support monitoring for conflicts between actual signal states and RSE communications about those states. |
| signal control commands | Control of traffic signal controllers or field masters including clock synchronization. |
| signal control device configuration | Data used to configure traffic signal control equipment including local controllers and system masters. |
| signal control plans | Traffic signal timing parameters including minimum green time and interval durations for basic operation and cycle length, splits, offset, phase sequence, etc. for coordinated systems. |
| signal control status | Operational and status data of traffic signal control equipment including operating condition and current indications. |
| signal system configuration | Data used to configure traffic signal systems including configuring control sections and mode of operation (time based or traffic responsive). |
| vehicle location and motion | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. |
| vehicle location and motion for surveillance | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. This flow represents monitoring of basic safety data ('vehicle location and motion') broadcast by passing connected vehicles for use in vehicle detection and traffic monitoring applications. |
Goals and Objectives
Associated Planning Factors and Goals
| Planning Factor | Goal |
|---|---|
| E. Protect and enhance the environment, promote energy conservation, improve the quality of life, and promote consistency between transportation improvements and State and local planned growth and economic development patterns; | Protect/Enhance the Environment |
Associated Objective Categories 
| Objective Category |
|---|
| Environment: Clean Air and Climate Change |
| System Efficiency: Energy Consumption |
Associated Objectives and Performance Measures 

Needs and Requirements
| Need | Functional Object | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. | Roadway Signal Control | 01 | The field element shall control traffic signals under center control. |
| 04 | The field element shall report the current signal control information to the center. | |||
| 13 | The field element shall provide to roadside equipment the intersection geometry and signal phase movement information including phase and timing information, alarm status, and priority/preempt status. | |||
| RSE Intersection Management | 01 | The field element shall communicate with passing vehicles to provide the current signal phase and timing information for all lanes and approaches at a signalized intersection. | ||
| 03 | The field element shall send the infrastructure application status to the operations center. | |||
| 09 | The field element shall collect current signal phase and timing data from the traffic signal controller. | |||
| RSE Traffic Monitoring | 01 | The field element shall communicate with on-board equipment on passing vehicles to collect current vehicle position, speed, and heading and a record of previous events (e.g., starts and stops, link travel times) that can be used to determine current traffic conditions. | ||
| TIC Traffic Control Dissemination | 03 | The center shall provide real time signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection to vehicle. | ||
| TMC Signal Control | 01 | The center shall remotely control traffic signal controllers. | ||
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication | 06 | The vehicle shall exchange location and motion information with roadside equipment and nearby vehicles. | ||
| 07 | The vehicle shall receive warnings, informational road signs, traffic meters, and signals provided by infrastructure devices. | |||
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist | 01 | The vehicle shall receive the current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. | ||
| 02 | The vehicle drivers need their connected vehicle to provide recommendations for movement approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicle's operations. | RSE Intersection Management | 01 | The field element shall communicate with passing vehicles to provide the current signal phase and timing information for all lanes and approaches at a signalized intersection. |
| 09 | The field element shall collect current signal phase and timing data from the traffic signal controller. | |||
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist | 02 | The vehicle shall provide recommendations for movement approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to pass the next traffic signal on green or to decelerate to a stop in the most eco-friendly manner. | ||
| 03 | The connected vehicle needs to be able to automatically adjust its operating parameters approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to reduce the environmental impact of the vehicle's operation. | Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist | 03 | The vehicle shall automatically adjust its operating parameters approaching or departing a signalized intersection. |
Related Sources
| Document Name | Version | Publication Date |
|---|---|---|
| CO-UMP Green Light Optimal Speed Advisory | 5/31/2021 | |
| Eco-Signal Operations: Operational Concept | Final | 10/1/2013 |
| SAE J3067- Candidate Improvements to Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) Message Set Dictionary (SAE J2735)Using Systems Engineering Methods | 8/15/2014 |
Security
In order to participate in this service package, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Moderate | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Moderate | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Other Vehicles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Traffic Management Center | Moderate | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Transportation Information Center | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate | Class 1 |
| Vehicle | Low | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
In order to participate in this service package, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | intersection status monitoring | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This information could be ascertained by examining the signal states, and so is effectively broadcast. | If this is compromised, the RSE could send incorrect data to the Roadway Equipment. Since the data contained herein directly affects human safety, the Roadway Equipment may react to tell the RSE it is in conflict, which in turn may result in the RSE modifying or disabling its outputs. DISC THEA: info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered so the ITS RE has correct SPaT info for all lanes to be able to detect conflicts and support failsafe operating mode. DISC: THEA belives this may be HIGH for ISIG. NYC also believes this to be HIGH for PED-SIG. | A delay in reporting this may allow the RSE to distribute faulty information, but that information is contradicted by the signal state. Since there are multiple pathways for the information to be obtained, this is not 'High. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Traffic Management Center | intersection management application status | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| This information could be of interest to a malicious individual who is attempting to determine the best way to accomplish a crime. As such it would be best to not make it easily accessible. May be LOW in some cases. | If this is compromised, it could send unnecessary maintenance workers, or worse report plausible data that is erroneous. From THEA: should be able to cope with some bad information on the status and record of alerts/warnings; aggregate info; however could cause appearance of excessive traffic violations or unnecessary maintenance caused if data is compromised (operational state, status, log); should not affect the application functionality | Incident status information should be presented in timely fashion as large scale mobility and safety issues are related. There are other mechanisms for reporting this information however, thus MODERATE. From THEA: Only limited adverse effect of info is not timely/readily available | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Vehicle | intersection geometry | Low | High | Moderate |
| Map data intended for general use by any C-ITS component than needs it. No information here includes PII or anything else that, if viewed by someone other than the participant, would lead to harm. | Map data is used for a host of application purposes. This widespread use means that any corruption in the data has a widespread and far reaching effect. | Occasional outages of this flow will delay updates and lead to a loss of accurate function of some applications. Depending on the application this could be HIGH. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Vehicle | intersection status | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intended for all vehicles in the immediate area of the sender. | If this is compromised, the Vehicle OBE will receive messages that are inconsistent with what the traffic signals are displaying. This could lead to confusion and reduce the ability of the application to provide value. | If this is down, the Vehicle OBE doesn't get the information it needs to stay in synch with the actual signal state, reducing or eliminating the value add from having this application. We assume that the Vehicle OBE will detect a lack of availability and choose not to send out-of-date information, so a failure of availability cannot have worse consequences than a failure of integrity which we have previously assessed at MEDIUM. | |||
| Driver | Vehicle | driver input | Moderate | High | High |
| Data included in this flow may include origin and destination information, which should be protected from other's viewing as it may compromise the driver's privacy. | Commands from from the driver to the vehicle must be correct or the vehicle may behave in an unpredictable and possibly unsafe manner | Commands must always be able to be given or the driver has no control. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | conflict monitor status | Low | High | Moderate |
| This information could be ascertained by examining the signal states, and so is effectively broadcast. From NYC: This flow tells the RSE that the traffic controller is in a failed state – typically flashing signals not timing. | If this is compromised, it could send incorrect data to the RSE. Since the data contained herein directly affects human safety, the RSE may react to modify its outputs, at the least disabling related outputs. if compromised, the ITS RE may not be able to support failsafe operating mode in the event of a conflict between the ITS RE and RSE. May not be 'High' because the signal state is also present. From NYC: This flow tells the RSE that the traffic controller is in a failed state – typically flashing signals not timing. | A delay in reporting this may allow the RSE to distribute faulty information, but that information is contradicted by the signal state. Since there are multiple pathways for the information to be obtained, this is not 'High.' | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | intersection control status | Low | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | If this is compromised, the Roadway Equipment and Roadside Equipment will be sending messages that are inconsistent with each other, leading to confusion and possible accidents. | If this is down, the RSE doesn't get the information it needs to stay in synch with the actual signal state, reducing or eliminating the value add from having this application. The RSE must detect a lack of availability and choose not to send out-of-date information, so a failure of availability could be interpreted as having the same value as Integrity. However, this data is semi-predictable and there are other indicators (such as the lights themselves) of the intersection status. From NYC, who believe this should be HIGH for some applications: If this is down, the RSE doesn't get the information it needs to stay in synch with the actual signal state, reducing or eliminating the value add from having this application. The RSE must detect a lack of availability and choose not to send out-of-date information, so a failure of availability cannot have worse consequences than a failure of integrity which we have previously assessed at HIGH. |
|||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Driver | driver information | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is sent to all drivers and is also directly observable, by design. | This is the primary signal trusted by the driver to decide whether to go through the intersection and what speed to go through the intersection at; if it's wrong, accidents could happen. | If the lights are out you have to get a policeman to direct traffic – expensive and inefficient and may cause a cascading effect due to lack of coordination with other intersections. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Traffic Management Center | signal control status | Low | High | Moderate |
| The current conditions of an ITS RE are completely observable, by design. | This influences the TMC response to a right-of-way request. It should be as accurate as the right-of-way request themselves. For some applications (ISIG) this need only be moderate. Per THEA: info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered to enable effective monitoring and control by the TMC. DISC: THEA believes this to be MODERATE: "info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered to enable effective monitoring and control by the TMC; should be as accurate as the right of way request". NYC:TMC doesn't play an active role in this application, i.e. even if the information contained in this flow were incorrect, it is unlikely to affect the outcome of this application one way or the other. On some applications NYC has this MODERATE though. RES: This value can obviously change a lot depending on the application context. | The TMC will need the current status of the ITS RE in order to make an educated decision. If it is unavailable, the system is unable to operate. However, a few missed messages will not have a catastrophic impact. From NYC: TMC doesn't play an active role in this application, i.e. even if it is unavailable, it is unlikely to affect the outcome of this application one way or the other. RES: This value can change a lot depending on the application context. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | vehicle location and motion | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. Much of its information content can also be determined via other visual indicators | BSM info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered with | BSM must be broadcast regularly to make data available for other vehicle OBEs, but availability cannot be guaranteed over a wireless medium | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | intersection management application info | Moderate | High | Low |
| proprietary configuration data with warning parameters and thresholds | should be accurate and not be tampered with; could enable outside control of application | should be timely and readily available or may not be able to restart/reset; however, should be able to operate on a default configuration and/or stop sending messages | |||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | signal control commands | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should be kept confidential to minimize attack vectors. While an individual installation may not be particularly impacted by a cyberattack of its sensor network, another installation might be severely impacted, and different installations are likely to use similar methods, so compromising one leads to compromising all. DISC: NYC believes this to be LOW: "The result of this will be directly observable." | Invalid messages could lead to an unauthorized user gaining control of an intersection. This could also be used to bring traffic to a standstill, which could lead to a large financial impact on the community. DISC: NYC believes this to be MODERATE: The signal timing is critical to the intersection operation; incorrect signal timing can lead to significant congestion and unreliable operation; while unsafe operation is controlled by the cabinet monitoring system, attackers could "freeze" the signal or call a preemption. RES: This will vary depending on the application and implementation. | These messages are important to help with preemption and signal priority applications. Without them, these applications mayl not work. However, if these signals are not received, the ITS RE will continue to function using its default configuration. The TMC should have an acknowledgement of the receipt of a message. DISC: NYC blieves this to be LOW: TMC doesn't play an active role in this application, i.e. even if it is unavailable, it is unlikely to affect the outcome of this application one way or the other. RES: This will vary depending on the application and implementation. |
|||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | signal control device configuration | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should be kept confidential to minimize attack vectors. While an individual installation may not be particularly impacted by a cyberattack of its sensor network, another installation might be severely impacted, and different installations are likely to use similar methods, so compromising one leads to compromising all. DISC: THEA believes this to be LOW: "encrypted, authenticated, proprietary; however will not cause harm if seen, traffic light information is visible." | Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should have MODERATE integrity at minimum, just to guarantee that intended control messages are received. Incorrect, corrupted, intercepted and modified control messages can or will result in target field devices not behaving according to operator intent. The severity of this depends on the type of device, which is why some devices are set MODERATE and some HIGH. From THEA: proprietary info that should not be tampered with; includes local controllers and system masters; tampering with configurations could cause delays along with major safety issues | Control flow availability is related to the criticality of being able to remotely control the device. For most devices, this is MODERATE. For purely passive devices with no incident relationship, this will be LOW. All devices should have default modes that enable them to operate without backhaul connectivity, so no device warrants a HIGH. From THEA: should be timely and readily available; however, should be able to function using a default configuration | |||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | signal control plans | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should be kept confidential to minimize attack vectors. While an individual installation may not be particularly impacted by a cyberattack of its sensor network, another installation might be severely impacted, and different installations are likely to use similar methods, so compromising one leads to compromising all. DISC: THEA believes this to be LOW: "encrypted, authenticated, proprietary; but the result is directly observable from traffic lights | Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should have MODERATE integrity at minimum, just to guarantee that intended control messages are received. Incorrect, corrupted, intercepted and modified control messages can or will result in target field devices not behaving according to operator intent. The severity of this depends on the type of device, which is why some devices are set MODERATE and some HIGH. From THEA: proprietary info that should not be tampered with; tampering with these plans could cause delays along with major safety issues | Control flow availability is related to the criticality of being able to remotely control the device. For most devices, this is MODERATE. For purely passive devices with no incident relationship, this will be LOW. All devices should have default modes that enable them to operate without backhaul connectivity, so no device warrants a HIGH. From THEA: should be timely and readily available; coordinated with other systems; however, should be able to function using a default configuration | |||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | signal system configuration | Low | High | Moderate |
| encrypted, authenticated, proprietary; however, the result is directly observable from traffic lights | proprietary info that should not be tampered with; data used to configure traffic signal systems; could cause significant delays and traffic issues if compromised | should be readily available; configurations can be time | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transportation Information Center | intersection status | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is distributed using a variety of mechanisms, some of which are localized broadcast; it is desireable that all potential users get this information. | If this flow is not accurate or delivered in a timely fashion then a large variety of mobility and safety services that depend on it will not work properly. | If this flow is not accurate or delivered in a timely fashion then a large variety of mobility and safety services that depend on it will not work properly. | |||
| Transportation Information Center | Vehicle | intersection status | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is distributed using a variety of mechanisms, some of which are localized broadcast; it is desireable that all potential users get this information. | If this flow is not accurate or delivered in a timely fashion then a large variety of mobility and safety services that depend on it will not work properly. | If this flow is not accurate or delivered in a timely fashion then a large variety of mobility and safety services that depend on it will not work properly. | |||
| Vehicle | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | vehicle location and motion for surveillance | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This is directly observable data; DISC: WYO believes this to be MODERATE | Incorrect information here could lead to the system not functioning properly. If they are unable to properly detect all vehicles crossing the border, it would lead to confusion. There are other factors, such as visual indicators, of vehicles crossing the border, which can be used to help mitigate contradicting information. DISC: THEA believes this should be HIGH: "BSM info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered with" WYO believes this to be HIGH | This information must be available in a timely manner for the system to act upon it. The system can operate correctly if some messages are missed, but overall a majority of them should be received.; WYO believes this to be LOW | |||
| Vehicle | Driver | driver updates | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is informing the driver about the safety of a nearby area. It should not contain anything sensitive, and does not matter if another person can observe it. | This is the information that is presented to the driver. If they receive incorrect information, they may act in an unsafe manner. However, there are other indicators that would alert them to any hazards, such as an oncoming vehicle or crossing safety lights. | If this information is not made available to the driver, then the system has not operated correctly. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | vehicle location and motion | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. Much of its information content can also be determined via other visual indicators | BSM info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered with | BSM must be broadcast regularly to make data available for other vehicle OBEs, but availability cannot be guaranteed over a wireless medium | |||
Standards
The following table lists the standards associated with physical objects in this service package. For standards related to interfaces, see the specific information flow triple pages.
| Name | Title | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| CTI 4001 RSU | Roadside Unit (RSU) Standard | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment |
| ITE 5201 ATC | Advanced Transportation Controller | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| ITE 5202 ATC Model 2070 | Model 2070 Controller Standard | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| ITE 5301 ATC ITS Cabinet | Intelligent Transportation System Standard Specification for Roadside Cabinets | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| ITE 5401 ATC API | Application Programming Interface Standard for the Advanced Transportation Controller | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| NEMA TS 8 Cyber and Physical Security | Cyber and Physical Security for Intelligent Transportation Systems | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| Traffic Management Center | ||
| NEMA TS2 Traffic Controller Assemblies | Traffic Controller Assemblies with NTCIP Requirements | ITS Roadway Equipment |
System Requirements
| System Requirement | Need | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | The system shall provide real time signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection to vehicle. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 002 | The system shall remotely control traffic signal controllers. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 003 | The system shall control traffic signals under center control. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 004 | The system shall report the current signal control information to the center. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 005 | The system shall provide to roadside equipment the intersection geometry and signal phase movement information including phase and timing information, alarm status, and priority/preempt status. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 006 | The system shall communicate with passing vehicles to provide the current signal phase and timing information for all lanes and approaches at a signalized intersection. | 02 | The vehicle drivers need their connected vehicle to provide recommendations for movement approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicle's operations. |
| 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. | ||
| 007 | The system shall send the infrastructure application status to the operations center. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 008 | The system shall collect current signal phase and timing data from the traffic signal controller. | 02 | The vehicle drivers need their connected vehicle to provide recommendations for movement approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicle's operations. |
| 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. | ||
| 009 | The system shall communicate with on-board equipment on passing vehicles to collect current vehicle position, speed, and heading and a record of previous events (e.g., starts and stops, link travel times) that can be used to determine current traffic conditions. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 010 | The system shall exchange location and motion information with roadside equipment and nearby vehicles. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 011 | The system shall receive warnings, informational road signs, traffic meters, and signals provided by infrastructure devices. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 012 | The system shall receive the current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. | 01 | Traffic Operations needs to be able to provide both intersection geometry and signal phase and timing information to vehicles. |
| 013 | The system shall provide recommendations for movement approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to pass the next traffic signal on green or to decelerate to a stop in the most eco-friendly manner. | 02 | The vehicle drivers need their connected vehicle to provide recommendations for movement approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicle's operations. |
| 014 | The system shall automatically adjust its operating parameters approaching or departing a signalized intersection. | 03 | The connected vehicle needs to be able to automatically adjust its operating parameters approaching or departing a signalized intersection in order to reduce the environmental impact of the vehicle's operation. |
Implementations


ST08.1 Wide-Area Wireless Implementation
Short range communications is not available for individual intersections, so this implementation uses wide-area wireless (WAW) communications to provide current signal, phase, and timing information for intersections in the area to vehicles to support more efficient use of the intersections by approaching and queued vehicles. In this implementation, current traffic data is collected by traditional traffic detectors to optionally support adaptive signal operations that are reflected in the signal, phase, and timing information provided via WAW.
Wide-Area Wireless Implementation Flows
| Information Flow | Description | Inclusion Status |
|---|---|---|
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information provided to the driver to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. | Fundamental |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. | Optional |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. | Optional |
| intersection status | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow identifies active lanes and lanes that are being stopped and specifies the length of time that the current state will persist for each lane. It also identifies signal priority and preemption status and pedestrian crossing status information where applicable. | Fundamental |
| signal control commands | Control of traffic signal controllers or field masters including clock synchronization. | Optional |
| signal control device configuration | Data used to configure traffic signal control equipment including local controllers and system masters. | Optional |
| signal control plans | Traffic signal timing parameters including minimum green time and interval durations for basic operation and cycle length, splits, offset, phase sequence, etc. for coordinated systems. | Optional |
| signal control status | Operational and status data of traffic signal control equipment including operating condition and current indications. | Fundamental |
| signal system configuration | Data used to configure traffic signal systems including configuring control sections and mode of operation (time based or traffic responsive). | Optional |
Wide-Area Wireless Implementation Functional Objects
| Functional Object |
|---|
| Roadway Signal Control |
| TIC Traffic Control Dissemination |
| TMC Signal Control |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist |
Back to Implementation List
ST08.2 C-ITS Short Range Communications Implementation
Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment supports real-time communications between the intersection and approaching vehicles. Detailed status is collected from approaching vehicles and real-time intersection status is provided so that vehicles can optimize their intersection use. Signal timing is adapted based on the data collected from approaching vehicles.
C-ITS Short Range Communications Implementation Flows
| Information Flow | Description | Inclusion Status |
|---|---|---|
| conflict monitor status | A control flow that supports failsafe operation in the event that a conflict is detected that requires the RSE to enter a failsafe operating mode for intersection management. Analogous to a traffic signal conflict monitor, this flow is issued when differences are detected between information provided to the vehicle for in-vehicle display and information displayed by field devices. It contains the details of differences that were found. | Optional |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information provided to the driver to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. | Fundamental |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. | Optional |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. | Optional |
| intersection control status | Status data provided by the traffic signal controller including phase information, alarm status, and priority/preempt status. | Fundamental |
| intersection geometry | The physical geometry of an intersection covering the location and width of each approaching lane, egress lane, and valid paths between approaches and egresses. This flow also defines the location of stop lines, cross walks, specific traffic law restrictions for the intersection (e.g., turning movement restrictions), and other elements that support calculation of a safe and legal vehicle path through the intersection. | Fundamental |
| intersection management application info | Intersection and device configuration data, including intersection geometry, and warning parameters and thresholds. This flow also supports remote control of the application so the application can be taken offline, reset, or restarted. | Fundamental |
| intersection management application status | Infrastructure application status reported by the RSE. This includes current operational state and status of the RSE and a log of operations. | Fundamental |
| intersection status | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow identifies active lanes and lanes that are being stopped and specifies the length of time that the current state will persist for each lane. It also identifies signal priority and preemption status and pedestrian crossing status information where applicable. | Fundamental |
| intersection status monitoring | Current signal phase and timing information for all lanes at a signalized intersection. This flow represents monitoring of communications by a receiver at the intersection to support monitoring for conflicts between actual signal states and RSE communications about those states. | Fundamental |
| signal control commands | Control of traffic signal controllers or field masters including clock synchronization. | Optional |
| signal control device configuration | Data used to configure traffic signal control equipment including local controllers and system masters. | Optional |
| signal control plans | Traffic signal timing parameters including minimum green time and interval durations for basic operation and cycle length, splits, offset, phase sequence, etc. for coordinated systems. | Optional |
| signal control status | Operational and status data of traffic signal control equipment including operating condition and current indications. | Optional |
| signal system configuration | Data used to configure traffic signal systems including configuring control sections and mode of operation (time based or traffic responsive). | Optional |
| vehicle location and motion | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. | Optional |
| vehicle location and motion for surveillance | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. This flow represents monitoring of basic safety data ('vehicle location and motion') broadcast by passing connected vehicles for use in vehicle detection and traffic monitoring applications. | Optional |
C-ITS Short Range Communications Implementation Functional Objects
| Functional Object |
|---|
| Roadway Signal Control |
| RSE Intersection Management |
| RSE Traffic Monitoring |
| TMC Signal Control |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication |
| Vehicle Eco-Driving Assist |
Back to Implementation List
