VS03: Situational Awareness
This service package shares information about potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards with other vehicles to support enhanced driver warnings and control automation. Vehicles broadcast relevant road condition information that is collected by the vehicle, such as fog or icy roads. Infrastructure-based sensors are used to augment the situational awareness information collected by vehicles, if available. This service package supports the capability for connected vehicles to share situational awareness information even in areas where no roadside communications infrastructure exists. It can be useful to vehicles that are not fully equipped with sensors, or vehicles entering an area with hazardous conditions. Roadside communications infrastructure, if available, can extend the situational awareness range to cover wrong way vehicles where closing rates can require notification beyond short range wireless communications range.
Relevant Regions: Australia, Canada, European Union, and United States
- Enterprise
- Functional
- Physical
- Goals and Objectives
- Needs and Requirements
- Sources
- Security
- Standards
- System Requirements
Enterprise
Development Stage Roles and Relationships
Installation Stage Roles and Relationships
Operations and Maintenance Stage Roles and Relationships
(hide)
| Source | Destination | Role/Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Vehicle Maintainer | Basic Vehicle | Maintains |
| Basic Vehicle Manager | Basic Vehicle | Manages |
| Basic Vehicle Manager | Driver | System Usage Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Driver | Vehicle Operating Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Supplier | Basic Vehicle Owner | Warranty |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Maintains |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Manager | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Manages |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Vehicle Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Supplier | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Driver | Basic Vehicle | Operates |
| Driver | Roadway Owner | Expectation of Roadway Condition Management |
| Driver | Vehicle | Operates |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | ITS Roadway Equipment | Maintains |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | ITS Roadway Equipment | Manages |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Supplier | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Maintains |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Manager | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Manages |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Supplier | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Other Vehicles Maintainer | Other Vehicles | Maintains |
| Other Vehicles Manager | Other Vehicles | Manages |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Driver | Vehicle Operating Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Other Vehicles Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Other Vehicles Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Vehicle Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Other Vehicles Owner | Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Other Vehicles Supplier | Other Vehicles Owner | Warranty |
| Roadway Maintainer | Roadway Environment | Maintains |
| Roadway Manager | Roadway Environment | Manages |
| Roadway Owner | Roadway Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Roadway Owner | Roadway Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Vehicle Characteristics Maintainer | Vehicle Characteristics | Maintains |
| Vehicle Characteristics Manager | Vehicle Characteristics | Manages |
| Vehicle Characteristics Owner | Vehicle Characteristics Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Vehicle Characteristics Owner | Vehicle Characteristics Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Vehicle Characteristics Supplier | Vehicle Characteristics Owner | Warranty |
| Vehicle Maintainer | Vehicle | Maintains |
| Vehicle Manager | Driver | System Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Manager | Vehicle | Manages |
| Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Vehicle Owner | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Driver | Application Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Driver | Vehicle Operating Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Other Vehicles Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Other Vehicles Owner | Expectation of Data Provision |
| Vehicle Owner | Other Vehicles User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Vehicle Owner | Vehicle Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Vehicle Supplier | Vehicle Owner | Warranty |
Functional
This service package includes the following Functional View PSpecs:
Physical
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG.SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
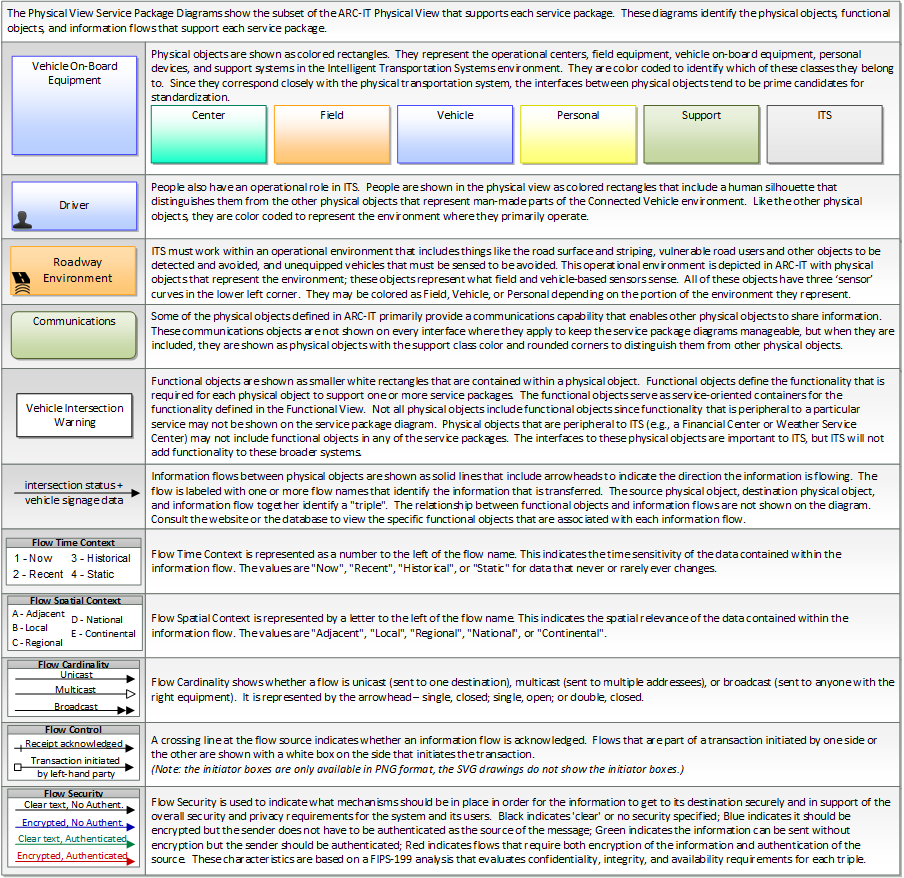
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Vehicle | Vehicle | 'Basic Vehicle' represents a complete operating vehicle. It includes the vehicle platform that interfaces with and hosts ITS electronics and all of the driver convenience and entertainment systems, and other non-ITS electronics on-board the vehicle. Interfaces represent both internal on-board interfaces between ITS equipment and other vehicle systems and other passive and active external interfaces or views of the vehicle that support vehicle/traffic monitoring and management. External interfaces may also represent equipment that is carried into the vehicle (e.g., a smartphone that is brought into the vehicle). Internal interfaces are often implemented through a vehicle databus, which is also included in this object. Note that 'Vehicle' represents the general functions and interfaces that are associated with personal automobiles as well as commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and other specialized vehicles. |
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Field | 'Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment' (CV RSE) represents the Connected Vehicle roadside devices (i.e., Roadside Units (RSUs)) equipped with short range wireless (SRW) communications technology, as well as any other supporting equipment that leverage the RSU and are not described by other objects (e.g., a local roadside processor). CVRSE are used to send messages to, and receive messages from, nearby vehicles and personal devices equipped with compatible communications technology. Communications with adjacent field equipment and back office centers that monitor and control the RSE are also supported. This device operates from a fixed position and may be permanently deployed or a portable device that is located temporarily in the vicinity of a traffic incident, road construction, or a special event. It includes a processor, data storage, and communications capabilities that support secure communications with passing vehicles, other field equipment, and centers. |
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway. This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Field | Representing another Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment, 'Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment' supports peer to peer communication and direct coordination between RSEs. It provides a source and destination for information that may be exchanged between RSEs. |
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | 'Other Vehicle OBEs' represents other connected vehicles that are communicating with the host vehicle. This includes all connected motorized vehicles including passenger cars, trucks, and motorcycles and specialty vehicles (e.g., maintenance vehicles, transit vehicles) that also include the basic 'Vehicle OBE' functionality that supports V2V communications. This object provides a source and destination for information transfers between connected vehicles. The host vehicle on-board equipment, represented by the Vehicle OBE physical object, sends information to, and receives information from the Other Vehicle OBEs to model all connected vehicle V2V communications in ARC-IT. |
| Potential Obstacles | Field | 'Potential Obstacles' represents any object that possesses the potential of being sensed and struck and thus also possesses physical attributes. Potential Obstacles include roadside obstructions, debris, animals, infrastructure elements (barrels, cones, barriers, etc.) or any other element that is in a potential path of the vehicle. Note that roadside objects and pieces of equipment that can become obstacles in a vehicle's path can include materials, coatings, or labels (e.g., barcodes) that will improve the performance of the vehicle-based sensors that must detect and avoid these obstacles. See also 'Vulnerable Road Users' that more specifically represents the physical properties of shared users of the roadway that must also be detected. |
| Roadway Environment | Field | 'Roadway Environment' represents the physical condition and geometry of the road surface, markings, signs, and other objects on or near the road surface. It also represents the environmental conditions immediately surrounding the roadway. The roadway environment must be sensed and interpreted to support automated vehicle services. Surrounding conditions may include fog, ice, snow, rain, wind, etc. which will influence the way in which a vehicle can be safely operated on the roadway. The roadway environment must be monitored to enable corrective action and information dissemination regarding roadway conditions which may adversely affect travel. Infrastructure owner/operators can improve the roadway environment to improve the performance and accuracy of vehicle-based sensors that must sense and interpret this environment. Improvements could include changes in the shape, size, design, and materials used in signs, pavement markings, and other road features. |
| Vehicle | Vehicle | This 'Vehicle' physical object is used to model core capabilities that are common to more than one type of Vehicle. It provides the vehicle-based general sensory, processing, storage, and communications functions that support efficient, safe, and convenient travel. Many of these capabilities (e.g., see the Vehicle Safety service packages) apply to all vehicle types including personal vehicles, commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and maintenance vehicles. From this perspective, the Vehicle includes the common interfaces and functions that apply to all motorized vehicles. The radio(s) supporting V2V and V2I communications are a key component of the Vehicle. Both one-way and two-way communications options support a spectrum of information services from basic broadcast to advanced personalized information services. Advanced sensors, processors, enhanced driver interfaces, and actuators complement the driver information services so that, in addition to making informed mode and route selections, the driver travels these routes in a safer and more consistent manner. This physical object supports all six levels of driving automation as defined in SAE J3016. Initial collision avoidance functions provide 'vigilant co-pilot' driver warning capabilities. More advanced functions assume limited control of the vehicle to maintain lane position and safe headways. In the most advanced implementations, this Physical Object supports full automation of all aspects of the driving task, aided by communications with other vehicles in the vicinity and in coordination with supporting infrastructure subsystems. |
| Vehicle Characteristics | Vehicle | 'Vehicle Characteristics' represents the external view of individual vehicles of any class from cars and light trucks up to large commercial vehicles and down to micromobility vehicles (MMVs). It includes vehicle physical characteristics such as height, width, length, weight, and other properties (e.g., magnetic properties, number of axles) of individual vehicles that can be sensed and measured or classified. This physical object represents the physical properties of vehicles that can be sensed by vehicle-based or infrastructure-based sensors to support vehicle automation and traffic sensor systems. The analog properties provided by this terminator represent the sensor inputs that are used to detect and assess vehicle(s) within the sensor's range to support safe AV operation and/or responsive and safe traffic management. |
| Vulnerable Road Users | Personal | 'Vulnerable Road Users' represents any roadway user not in a motorized vehicle capable of operating at the posted speed for the roadway in question, and also any roadway user in a vehicle not designed to encase (and thus protect) its occupants. This includes pedestrians, cyclists, wheelchair users, two-wheeled scooter micromobility users, as well as powered scooters and motorcycles. Note that this terminator represents the physical properties of vulnerable road users and their conveyance that may be sensed to support safe vehicle automation and traffic management in mixed mode applications where a variety of road users share the right-of-way. See also 'Pedestrian' and 'MMV User' Physical Objects that represent the human interface to these vulnerable road users. |
Includes Functional Objects:
| Functional Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Roadway Basic Surveillance | 'Roadway Basic Surveillance' monitors traffic conditions using fixed equipment such as loop detectors and CCTV cameras. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| Roadway Wrong Way Vehicle Detection | 'Roadway Wrong Way Vehicle Detection' provides wrong way vehicle detection using traffic detectors and surveillance equipment. It provides potential wrong way vehicle notifications as well as supporting detector data and images to the center for processing and presentation to traffic operations personnel. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| RSE Communications Relay | 'RSE Communications Relay' provides message relay services that extend effective communications range to improve communications systems performance and robustness. It also supports safety applications such as wrong way vehicle detection and other applications where roadside communication of warnings beyond DSRC range are needed to compensate for high speeds or line of site/RF interference challenges. | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment |
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication | 'Vehicle Basic Safety Communication' exchanges current vehicle characteristics, location, and motion (including past and intended maneuver) information with other vehicles in the vicinity, uses that information to calculate vehicle paths, and warns the driver when the potential for an impending collision is detected. If available, map data is used to filter and interpret the relative location and motion of vehicles in the vicinity. Information from on-board sensors (e.g., radars and image processing) are also used, if available, in combination with the V2V communications to detect non-equipped vehicles and corroborate connected vehicle data. This object represents a broad range of implementations ranging from basic Vehicle Awareness Devices that only broadcast vehicle location and motion and provide no driver warnings to advanced integrated safety systems that coordinate maneuvers and may, in addition to warning the driver, provide collision warning information to support automated control functions that can support control intervention. | Vehicle |
| Vehicle Control Automation | 'Vehicle Control Automation' provides lateral and/or longitudinal control of a vehicle to allow 'hands off' and/or 'feet off' driving, automating the steering, accelerator, and brake control functions. It builds on the sensors included in 'Vehicle Safety Monitoring' and 'Vehicle Control Warning' and uses the information about the area surrounding the vehicle to safely control the vehicle. It covers the range of incremental control capabilities from driver assistance systems that take over steering or acceleration/deceleration in limited scenarios with direct monitoring by the driver to full automation where all aspects of driving are automated under all roadway and environmental conditions. | Vehicle |
| Vehicle Control Warning | 'Vehicle Control Warning' monitors areas around the vehicle and provides warnings to a driver so the driver can take action to recover and maintain safe control of the vehicle. It includes lateral warning systems that warn of lane departures and obstacles or vehicles to the sides of the vehicle and longitudinal warning systems that monitor areas in the vehicle path and provide warnings when headways are insufficient or obstacles are detected in front of or behind the vehicle. It includes on-board sensors, including radars and imaging systems, and the driver information system that provides the visual, audible, and/or haptic warnings to the driver. | Vehicle |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| detected obstacles | Notification of a nearby non-vehicular object that does not appear to be equipped with a short range communications device but is detectable using onboard vehicle or infrastructure sensors. This could be anything from a construction barrel to a pedestrian or animal. The flow communicates detected object location, physical characteristics, observable kinematics and confidence in those measures. |
| detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Notification of a nearby vehicle (light vehicle, commercial vehicle, MMV etc.) or vulnerable road user that does not appear to be equipped with a short range communications device but is detectable using onboard vehicle or infrastructure sensors. The flow communicates detected vehicle/VRU location, physical characteristics, observable kinematics and confidence in those measures. |
| driver input | Driver input to the vehicle on-board equipment including configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands. |
| driver input information | Driver input received from the driver-vehicle interface equipment via the vehicle bus. It includes configuration data, settings and preferences, interactive requests, and control commands for the connected vehicle on-board equipment. |
| driver update information | Information provided to the driver-vehicle interface to inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. The flow includes the information to be presented to the driver and associated metadata that supports processing, prioritization, and presentation by the DVI as visual displays, audible information and warnings, and/or haptic feedback. |
| driver updates | Information provided to the driver including visual displays, audible information and warnings, and haptic feedback. The updates inform the driver about current conditions, potential hazards, and the current status of vehicle on-board equipment. |
| environmental conditions | Current road conditions (e.g., surface temperature, subsurface temperature, moisture, icing, treatment status) and surface weather conditions (e.g., air temperature, wind speed, precipitation, visibility) that are measured by environmental sensors. |
| host vehicle status | Information provided to the ITS on-board equipment from other systems on the vehicle platform. This includes the current status of the powertrain, steering, and braking systems, and status of other safety and convenience systems. In implementations where GPS is not integrated into the Vehicle On-Board Equipment, the host vehicle is also the source for data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions (latitude, longitude, elevation) and accurate time that can be used for time synchronization across the ITS environment. |
| physical presence | Detection of an obstacle. Obstacle could include animals, incident management and construction elements such as cones, barrels and barriers, rocks in roadway, etc. |
| roadway characteristics | Detectable or measurable road characteristics such as friction coefficient and general surface conditions, road geometry and markings, etc. These characteristics are monitored or measured by ITS sensors and used to support advanced vehicle safety and control and road maintenance capabilities. |
| vehicle characteristics | The physical or visible characteristics of individual vehicles that can be used to detect, classify, and monitor vehicles and imaged to uniquely identify vehicles. |
| vehicle control | Control commands issued to vehicle actuators that control steering, throttle, and braking and other related commands that support safe transition between manual and automated vehicle control. This flow can also deploy restraints and other safety systems when a collision is unavoidable. |
| vehicle control event | Notification that the vehicle has performed an emergency maneuver or action that could impact the safety of surrounding vehicles. This includes hard braking and activation of traction/stability control systems or other actions that warrant immediate notification of surrounding vehicles. The information flow conveys the current vehicle location, path, and current control actions. This may also include the list of maneuvers includes lane changes/departures and overtaking/passing maneuvers. |
| vehicle environmental data | Data from vehicle safety and convenience systems that can be used to estimate environmental and infrastructure conditions, including measured air temperature, exterior light status, wiper status, sun sensor status, rain sensor status, traction control status, anti-lock brake status, vertical acceleration and other collected vehicle system status and sensor information. The collected data is reported along with the location, heading, and time that the data was collected. Both current data and snapshots of recent events (e.g., traction control or anti-lock brake system activations) may be reported. |
| vehicle hazard event | Notification of a potential hazard based on an action or condition that the vehicle is currently performing or experiencing. Self-reported hazards include notification that the vehicle is being operated in an unsafe manner or is stopped in the travel lanes or on the shoulder. It includes vehicle location and status, path, current control actions, and additional information on the vehicle state, if applicable. This includes vehicles making excessive lane changes or traveling at excessive speeds, maintaining less than minimum headways, and wrong way vehicles. |
| vehicle location and motion | Data describing the vehicle's location in three dimensions, heading, speed, acceleration, braking status, and size. |
| vehicle path prediction | The predicted future vehicle path of travel. This flow includes an indication of the future positions of the transmitting vehicle that can be used by receiving vehicles to support coordinated driving maneuvers and enhance in-lane and out-of-lane threat classification. |
| vulnerable road user presence | Detection of pedestrians, cyclists, and other vulnerable road users. This detection is based on physical characteristics of the user and their conveyance, which may be enhanced by design and materials that facilitate sensor-based detection and tracking of vulnerable road users. |
| wrong way vehicle detected | Notification that a vehicle has been detected traveling in the wrong direction. This can be a direct report by an equipped vehicle that is being driven in the wrong direction or a report of a non-equipped vehicle that has been detected traveling in the wrong direction. It includes the current location, speed, acceleration, and heading of the wrong way vehicle. |
Goals and Objectives
Associated Planning Factors and Goals
| Planning Factor | Goal |
|---|---|
| B. Increase the safety of the transportation system for motorized and nonmotorized users; | Reduce fatalities and injuries |
Associated Objective Categories 
| Objective Category |
|---|
| Safety: Vehicle Crashes and Fatalities |
Associated Objectives and Performance Measures 

Needs and Requirements
| Need | Functional Object | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. | RSE Communications Relay | 01 | The field device shall be capable of relaying safety related messages, such as detection of wrong- way vehicles, to other connected vehicle field devices. |
| 02 | The field device shall be capable of relaying safety related messages, such as detection of wrong-way vehicles, to equipped vehicles. | |||
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication | 04 | The vehicle shall collect road condition data from other vehicles. | ||
| 10 | The vehicle shall determine the status of host vehicle systems including vehicle speed, heading, yaw, wheelspin, ABS, traction control, and wiper status. | |||
| 11 | The vehicle shall determine if vehicle systems status indicates a potentially hazardous road condition. | |||
| 14 | The vehicle shall determine if road conditions data received from other vehicles represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. | |||
| 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. | Roadway Basic Surveillance | 01 | The field element shall collect, process, digitize, and send traffic sensor data (speed, volume, and occupancy) to the center for further analysis and storage, under center control. |
| 02 | The field element shall collect, process, and send traffic images to the center for further analysis and distribution. | |||
| 04 | The field element shall return sensor and CCTV system operational status to the controlling center. | |||
| Roadway Wrong Way Vehicle Detection | 01 | The field element shall detect wrong way vehicle entry using traffic detectors and surveillance equipment. | ||
| 02 | The field equipment shall provide wrong way vehicle detection data to roadside communications equipment for sharing with upstream/downstream vehicles that may be impacted by the wrong way vehicle. | |||
| 03 | The field equipment shall provide potential wrong way vehicle detection data and images to the center for processing. | |||
| 03 | The Driver needs to be warned by the connected vehicle or have control actions taken based on information received regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards | RSE Communications Relay | 01 | The field device shall be capable of relaying safety related messages, such as detection of wrong- way vehicles, to other connected vehicle field devices. |
| 02 | The field device shall be capable of relaying safety related messages, such as detection of wrong-way vehicles, to equipped vehicles. | |||
| Vehicle Basic Safety Communication | 01 | The vehicle shall collect location and motion data from the vehicle platform. | ||
| Vehicle Control Automation | 11 | The vehicle shall perform control actions based on information received from other vehicles regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards. | ||
| Vehicle Control Warning | 05 | The vehicle shall provide warnings to the driver based on information received from other vehicles regarding potentially hazardous road conditions, road hazards, or pending/in-progress vehicle maneuvers. | ||
Related Sources
| Document Name | Version | Publication Date |
|---|---|---|
| ITS User Services Document | 1/1/2005 | |
| ETSI TR 102 638 ITS Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Definitions | 6/1/2009 | |
| ETSI TS 102 637-1 ITS Vehicular Communications; Basic Set of Applications; Part 1: Functional Requirements | 9/1/2010 | |
| SAE J3067- Candidate Improvements to Dedicated Short Range Communications (DSRC) Message Set Dictionary (SAE J2735)Using Systems Engineering Methods | 8/15/2014 |
Security
In order to participate in this service package, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Basic Vehicle | ||||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Not Applicable | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Not Applicable | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Not Applicable | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Other Vehicles | Low | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Potential Obstacles | ||||
| Roadway Environment | Not Applicable | Low | Low | Class 1 |
| Vehicle | Low | High | Moderate | Class 3 |
| Vehicle Characteristics | ||||
| Vulnerable Road Users | ||||
In order to participate in this service package, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| Basic Vehicle | Vehicle | driver input information | Moderate | High | High |
| Internal vehicle flow that if reverse engineered could enable third party vehicle control. Largely a competitive question, could be set LOW if manufacturer and operator are not concerned with this type of compromise. | Includes vehicle control commands, which must be timely and accurate to support safe vehicle operation. | Includes vehicle control commands, which must be timely and accurate to support safe vehicle operation. | |||
| Basic Vehicle | Vehicle | host vehicle status | Low | Moderate | High |
| Unlikely that this includes any information that could be used against the originator. | This can be MODERATE or HIGH, depending on the application: This is used later on to determine whether a vehicle is likely going to violate a red light or infringe a work zone. This needs to be correct in order for the application to work correctly. | Since this monitors the health and safety of the vehicle and that information is eventually reported to the driver, it should be available at all times as it directly affects vehicle and operator safety. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | detected obstacles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data could eventually be transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Vehicle | detected obstacles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Vehicle | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Vehicle | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Driver | Vehicle | driver input | Moderate | High | High |
| Data included in this flow may include origin and destination information, which should be protected from other's viewing as it may compromise the driver's privacy. | Commands from from the driver to the vehicle must be correct or the vehicle may behave in an unpredictable and possibly unsafe manner | Commands must always be able to be given or the driver has no control. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | detected obstacles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data could eventually be transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Other Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | detected obstacles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | vehicle control event | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard and should not be easy to forge. False messages here may lead to confusion that causes a traffic accident. From NYC: Integrity would need to be high if there were no mitigations against bad data in incoming BSMs. In fact, there are two mitigations: plausibility checking, and misbehavior reporting plus revocation. Taking these into account we believe, with [18], that the security requirements are met by requiring an integrity level of MODERATE on these information flows. RES: Sided with NYC due to mitigation documentation. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard. If it isn't received it increases the risk to other road users. If a vehicle is infringing on an intersection, it must report this. From NYC: Even moderate availability of BSMs will enable a large majority of collisions between equipped vehicles to be avoided. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | vehicle environmental data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Little abusive potential for capturing the information in this flow as designed. Could be moderate if this contains PII related information, but considered for now to not include any PII; DISC: WYO believes Vehicle to Center versions of this flow to be MODERATE as center penetrations could more easily garner aggregate user data that might be used for mischief. | This could be used for safety applications, and in areas of severe weather a corrupted field could have significant consequences; however, any vehicle will use other inputs before triggering automatic safety facilities, so MODERATE should be sufficient. DISC: WYO believes this to be HIGH. | This data is required for the system to operate properly. If this data is not available, the system cannot give accurate warning information. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | vehicle hazard event | Low | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard and should not be easy to forge. False messages here may lead to confusion that causes a traffic accident. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard. If it isn't received it increases the risk to other road users. If a vehicle is infringing on an intersection, it must report this. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | vehicle location and motion | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. Much of its information content can also be determined via other visual indicators | BSM info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered with | BSM must be broadcast regularly to make data available for other vehicle OBEs, but availability cannot be guaranteed over a wireless medium | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | vehicle path prediction | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to other vehicles operating in a cluster. | Vehicle path data is critical to the performance of a group of vehicles in a vehicle cluster scenario. Incorrect data here could trigger a severe accident scenario. | Some vehicle cluster scenarios cannot function without this flow. Worst case is that some vehicles will drop from the platoon however, which while significant to mobility does not have a direct severe consequence. | |||
| Other Vehicles | Vehicle | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Roadway Environment | Vehicle | environmental conditions | Not Applicable | Low | Low |
| Sensor-based information flows by definition have no confidentiality concerns. | While typically security concerns related to sensing ignored, if considered this would be LOW, as the obfuscation or failure of any given environmental sensor is likely to be overcome by the mass of data necessary to draw environmental concluisions. | While typically security concerns related to sensing ignored, if considered this would be LOW, as the obfuscation or failure of any given environmental sensor is likely to be overcome by the mass of data necessary to draw environmental concluisions. | |||
| Roadway Environment | Vehicle | roadway characteristics | Not Applicable | Low | Low |
| Sensor-based information flows by definition have no confidentiality concerns. | While typically security concerns related to sensing ignored, if considered this would be LOW, as the obfuscation or failure of any given environmental sensor is likely to be overcome by the mass of data necessary to draw environmental concluisions. | While typically security concerns related to sensing ignored, if considered this would be LOW, as the obfuscation or failure of any given environmental sensor is likely to be overcome by the mass of data necessary to draw environmental concluisions. | |||
| Vehicle | Basic Vehicle | driver update information | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This information is all presented to the vehicle operator. Encrypting this information may make it harder to reverse engineer vehicle systems, and may defeat criminal tracking tools when the vehicle has already been compromised. Unless those scenarios are of concern to the operator or manufacturer, this can safely be set LOW. | Any information presented to the operator of a vehicle should be both accurate and timely. By definition this includes safety information, but given that the driver has other means of learning about most threats, it seems difficult to justify HIGH. If HIGH is warranted, it should apply to both availability and integrity. | Any information presented to the operator of a vehicle should be both accurate and timely. By definition this includes safety information, but given that the driver has other means of learning about most threats, it seems difficult to justify HIGH. If HIGH is warranted, it should apply to both availability and integrity. | |||
| Vehicle | Basic Vehicle | vehicle control | Moderate | High | High |
| Internal vehicle flow that if reverse engineered could enable third party vehicle control. Largely a competitive question, could be set LOW if manufacturer and operator are not concerned with this type of compromise. | Includes vehicle control commands, which must be timely and accurate to support safe vehicle operation. | Includes vehicle control commands, which must be timely and accurate to support safe vehicle operation. | |||
| Vehicle | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | detected obstacles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Vehicle | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Vehicle | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
| Vehicle | Driver | driver updates | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is informing the driver about the safety of a nearby area. It should not contain anything sensitive, and does not matter if another person can observe it. | This is the information that is presented to the driver. If they receive incorrect information, they may act in an unsafe manner. However, there are other indicators that would alert them to any hazards, such as an oncoming vehicle or crossing safety lights. | If this information is not made available to the driver, then the system has not operated correctly. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | detected obstacles | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | detected unequipped vehicles and VRUs | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intended to be shared with all nearby vehicles, traffic control devices and vulnerable road users; it is essentially public. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. If manipulated or incorrect, a crash may occur; though vehicles able to use this data also have sensory capabilities, this flow will often contain data describing objects/vehicles/VRUs that are obscured and not observable by on-board sensors. | This data may be used as input to vehicle situational awareness and thus trigger crash-avoidance actions. This data enable collision avoidance actions that are impractical without it, as vehicles able to use this data to sense-by-proxy other vehicles/VRUs/obstacles that are obscured by on-board sensors. Considered MODERATE and not HIGH only because the lack of availability reverts to existing operations and does not actively make safety worse. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | vehicle control event | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | BSM info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered with, suggesting HIGH. From NYC: Integrity would need to be high if there were no mitigations against bad data in incoming BSMs. In fact, there are two mitigations: plausibility checking, and misbehavior reporting plus revocation. Taking these into account we believe, with [18], that the security requirements are met by requiring an integrity level of MODERATE on these information flows. RES: Sided with NYC due to mitigation documentation. | BSM must be broadcast regularly to make data available for other vehicle OBEs, but cannot guarantee wireless communication | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | vehicle environmental data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Little abusive potential for capturing the information in this flow as designed. Could be moderate if this contains PII related information, but considered for now to not include any PII; DISC: WYO believes Vehicle to Center versions of this flow to be MODERATE as center penetrations could more easily garner aggregate user data that might be used for mischief. | This could be used for safety applications, and in areas of severe weather a corrupted field could have significant consequences; however, any vehicle will use other inputs before triggering automatic safety facilities, so MODERATE should be sufficient. DISC: WYO believes this to be HIGH. | This data is required for the system to operate properly. If this data is not available, the system cannot give accurate warning information. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | vehicle hazard event | Low | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard and should not be easy to forge. False messages here may lead to confusion that causes a traffic accident. | This message is an indication of a potential hazard. If it isn't received it increases the risk to other road users. If a vehicle is infringing on an intersection, it must report this. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | vehicle location and motion | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. Much of its information content can also be determined via other visual indicators | BSM info needs to be accurate and should not be tampered with | BSM must be broadcast regularly to make data available for other vehicle OBEs, but availability cannot be guaranteed over a wireless medium | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | vehicle path prediction | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to other vehicles operating in a cluster. | Vehicle path data is critical to the performance of a group of vehicles in a vehicle cluster scenario. Incorrect data here could trigger a severe accident scenario. | Some vehicle cluster scenarios cannot function without this flow. Worst case is that some vehicles will drop from the platoon however, which while significant to mobility does not have a direct severe consequence. | |||
| Vehicle | Other Vehicles | wrong way vehicle detected | Not Applicable | Moderate | Moderate |
| This data is intentionally transmitted to everyone via a broadcast. It can also be determined via other visual indicators. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | This information could lead directly to an severe incident, however other mechanisms exist to confirm this data, thus availability and integrity are set to MODERATE instead of HIGH. | |||
Standards
The following table lists the standards associated with physical objects in this service package. For standards related to interfaces, see the specific information flow triple pages.
| Name | Title | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| CTI 4001 RSU | Roadside Unit (RSU) Standard | Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment |
| ITE 5301 ATC ITS Cabinet | Intelligent Transportation System Standard Specification for Roadside Cabinets | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| NEMA TS 8 Cyber and Physical Security | Cyber and Physical Security for Intelligent Transportation Systems | ITS Roadway Equipment |
System Requirements
| System Requirement | Need | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | The system shall relay safety related messages, such as detection of wrong-way vehicles, to other connected vehicle field devices. | 03 | The Driver needs to be warned by the connected vehicle or have control actions taken based on information received regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards |
| 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. | ||
| 002 | The system shall collect, process, digitize, and send traffic sensor data (speed, volume, and occupancy) to the center for further analysis and storage, under center control. | 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. |
| 003 | The system shall relay safety related messages, such as detection of wrong-way vehicles, to equipped vehicles. | 03 | The Driver needs to be warned by the connected vehicle or have control actions taken based on information received regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards |
| 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. | ||
| 004 | The system shall collect, process, and send traffic images to the center for further analysis and distribution. | 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. |
| 005 | The system shall return sensor and CCTV system operational status to the controlling center. | 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. |
| 006 | The system shall collect road condition data from other vehicles. | 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. |
| 007 | The system shall detect wrong way vehicle entry using traffic detectors and surveillance equipment. | 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. |
| 008 | The system shall collect location and motion data from the vehicle platform. | 03 | The Driver needs to be warned by the connected vehicle or have control actions taken based on information received regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards |
| 009 | The system shall provide wrong way vehicle detection data to roadside communications equipment for sharing with upstream/downstream vehicles that may be impacted by the wrong way vehicle. | 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. |
| 010 | The system shall determine the status of host vehicle systems including vehicle speed, heading, yaw, wheelspin, ABS, traction control, and wiper status. | 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. |
| 011 | The system shall provide potential wrong way vehicle detection data and images to the center for processing. | 02 | The Driver needs to be aware of road conditions or road hazards that are identified by infrastructure-based sensors, if available. |
| 012 | The system shall determine if vehicle systems status indicates a potentially hazardous road condition. | 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. |
| 013 | The system shall determine if road conditions data received from other vehicles represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. | 01 | The Driver needs to be able to receive indications of road conditions measured by remote vehicles that represent a potential safety hazard for the vehicle. |
| 014 | The system shall perform control actions based on information received from other vehicles regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards. | 03 | The Driver needs to be warned by the connected vehicle or have control actions taken based on information received regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards |
| 015 | The system shall provide warnings to the driver based on information received from other vehicles regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards. | 03 | The Driver needs to be warned by the connected vehicle or have control actions taken based on information received regarding potentially hazardous road conditions or road hazards |
