TM06: Traffic Information Dissemination
This service package provides driver information using roadway equipment such as dynamic message signs or highway advisory radio. A wide range of information can be disseminated including traffic and road conditions, closure and detour information, travel restrictions, incident information, and emergency alerts and driver advisories. This package provides information to drivers at specific equipped locations on the road network. Careful placement of the roadway equipment provides the information at points in the network where the drivers have recourse and can tailor their routes to account for the new information. This package also covers the equipment and interfaces that provide traffic information from a traffic management center to the media (for instance via a direct tie-in between a traffic management center and radio or television station computer systems), Transit Management, Emergency Management, and Transportation Information Centers. A link to the Maintenance and Construction Management Center allows real time information on road/bridge closures and restrictions due to maintenance and construction activities to be disseminated.
Relevant Regions: Australia, Canada, European Union, and United States
- Enterprise
- Functional
- Physical
- Goals and Objectives
- Needs and Requirements
- Sources
- Security
- Standards
- System Requirements
- Implementations
Enterprise
Development Stage Roles and Relationships
Installation Stage Roles and Relationships
Operations and Maintenance Stage Roles and Relationships
(hide)
| Source | Destination | Role/Relationship |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Vehicle Maintainer | Basic Vehicle | Maintains |
| Basic Vehicle Manager | Basic Vehicle | Manages |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Owner | Basic Vehicle Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Basic Vehicle Supplier | Basic Vehicle Owner | Warranty |
| Emergency Management Center Maintainer | Emergency Management Center | Maintains |
| Emergency Management Center Manager | Emergency Management Center | Manages |
| Emergency Management Center Owner | Emergency Management Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Emergency Management Center Owner | Emergency Management Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Emergency Management Center Supplier | Emergency Management Center Owner | Warranty |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | ITS Roadway Equipment | Maintains |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | ITS Roadway Equipment | Manages |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Basic Vehicle Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Basic Vehicle Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Basic Vehicle User | Service Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Other ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Other ITS Roadway Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Management Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Traffic Operations Personnel | Application Usage Agreement |
| ITS Roadway Equipment Supplier | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Maint and Constr Management Center Maintainer | Maint and Constr Management Center | Maintains |
| Maint and Constr Management Center Manager | Maint and Constr Management Center | Manages |
| Maint and Constr Management Center Owner | Maint and Constr Management Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Maint and Constr Management Center Owner | Maint and Constr Management Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Maint and Constr Management Center Supplier | Maint and Constr Management Center Owner | Warranty |
| Media Maintainer | Media | Maintains |
| Media Manager | Media | Manages |
| Media Owner | Media Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Media Owner | Media Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Media Supplier | Media Owner | Warranty |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Other ITS Roadway Equipment | Maintains |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | Other ITS Roadway Equipment | Manages |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Exchange and Action Agreement |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Other ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Other ITS Roadway Equipment Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment Supplier | Other ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Warranty |
| Traffic Management Center Maintainer | Traffic Management Center | Maintains |
| Traffic Management Center Manager | Traffic Management Center | Manages |
| Traffic Management Center Manager | Traffic Operations Personnel | System Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Emergency Management Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Emergency Management Center Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Emergency Management Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | ITS Roadway Equipment User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Maint and Constr Management Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Maint and Constr Management Center Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Maint and Constr Management Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Media Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Media Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Media User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Traffic Management Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Traffic Management Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transit Management Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transit Management Center Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transit Management Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Maintainer | Maintenance Data Exchange Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Owner | Information Provision Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Owner | Transportation Information Center User | Service Usage Agreement |
| Traffic Management Center Supplier | Traffic Management Center Owner | Warranty |
| Traffic Operations Personnel | Traffic Management Center | Operates |
| Transit Management Center Maintainer | Transit Management Center | Maintains |
| Transit Management Center Manager | Transit Management Center | Manages |
| Transit Management Center Owner | Transit Management Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Transit Management Center Owner | Transit Management Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Transit Management Center Supplier | Transit Management Center Owner | Warranty |
| Transportation Information Center Maintainer | Transportation Information Center | Maintains |
| Transportation Information Center Manager | Transportation Information Center | Manages |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Maintainer | System Maintenance Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Owner | Transportation Information Center Manager | Operations Agreement |
| Transportation Information Center Supplier | Transportation Information Center Owner | Warranty |
Functional
This service package includes the following Functional View PSpecs:
Physical
The physical diagram can be viewed in SVG or PNG format and the current format is SVG.SVG Diagram
PNG Diagram
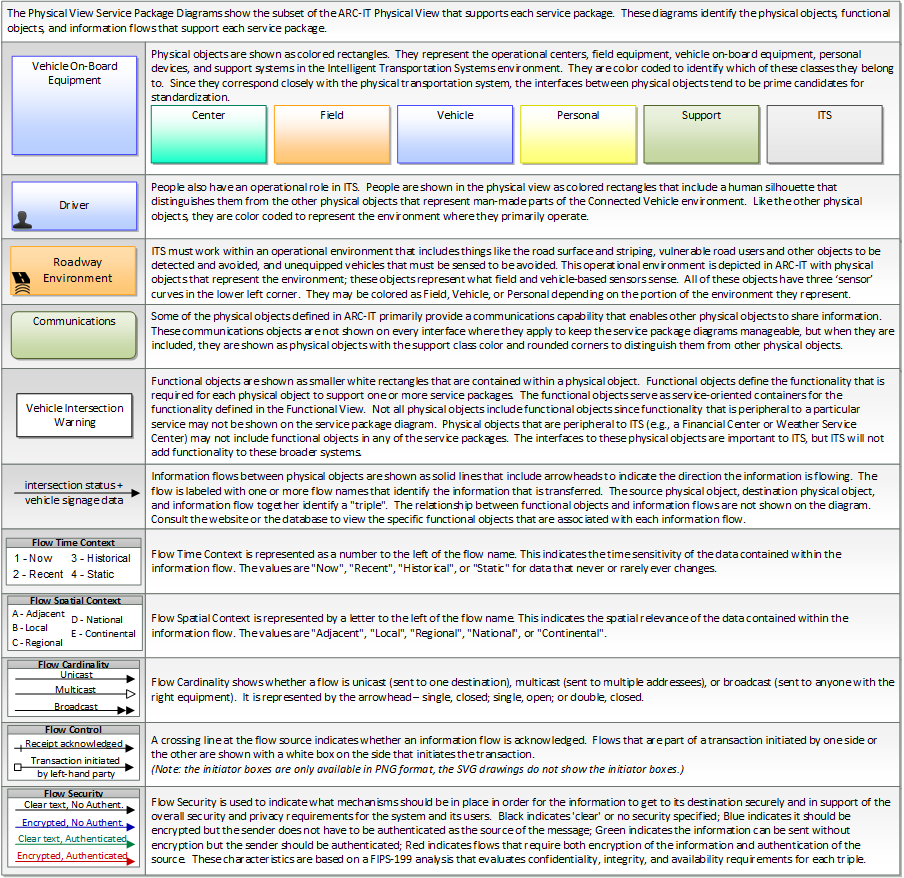
Includes Physical Objects:
| Physical Object | Class | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Vehicle | Vehicle | 'Basic Vehicle' represents a complete operating vehicle. It includes the vehicle platform that interfaces with and hosts ITS electronics and all of the driver convenience and entertainment systems, and other non-ITS electronics on-board the vehicle. Interfaces represent both internal on-board interfaces between ITS equipment and other vehicle systems and other passive and active external interfaces or views of the vehicle that support vehicle/traffic monitoring and management. External interfaces may also represent equipment that is carried into the vehicle (e.g., a smartphone that is brought into the vehicle). Internal interfaces are often implemented through a vehicle databus, which is also included in this object. Note that 'Vehicle' represents the general functions and interfaces that are associated with personal automobiles as well as commercial vehicles, emergency vehicles, transit vehicles, and other specialized vehicles. |
| Driver | Vehicle | The 'Driver' represents the person that operates a vehicle on the roadway. Included are operators of private, transit, commercial, and emergency vehicles where the interactions are not particular to the type of vehicle (e.g., interactions supporting vehicle safety applications). The Driver originates driver requests and receives driver information that reflects the interactions which might be useful to all drivers, regardless of vehicle classification. Information and interactions which are unique to drivers of a specific vehicle type (e.g., fleet interactions with transit, commercial, or emergency vehicle drivers) are covered by separate objects. |
| Emergency Management Center | Center | The 'Emergency Management Center' represents systems that support incident management, disaster response and evacuation, security monitoring, and other security and public safety-oriented ITS applications. It includes the functions associated with fixed and mobile public safety communications centers including public safety call taker and dispatch centers operated by police (including transit police), fire, and emergency medical services. It includes the functions associated with Emergency Operations Centers that are activated at local, regional, state, and federal levels for emergencies and the portable and transportable systems that support Incident Command System operations at an incident. This Center also represents systems associated with towing and recovery, freeway service patrols, HAZMAT response teams, and mayday service providers. It manages sensor and surveillance equipment used to enhance transportation security of the roadway infrastructure (including bridges, tunnels, interchanges, and other key roadway segments) and the public transportation system (including transit vehicles, public areas such as transit stops and stations, facilities such as transit yards, and transit infrastructure such as rail, bridges, tunnels, or bus guideways). It provides security/surveillance services to improve traveler security in public areas not a part of the public transportation system. It monitors alerts, advisories, and other threat information and prepares for and responds to identified emergencies. It coordinates emergency response involving multiple agencies with peer centers. It stores, coordinates, and utilizes emergency response and evacuation plans to facilitate this coordinated response. Emergency situation information including damage assessments, response status, evacuation information, and resource information are shared The Emergency Management Center also provides a focal point for coordination of the emergency and evacuation information that is provided to the traveling public, including wide-area alerts when immediate public notification is warranted. It tracks and manages emergency vehicle fleets using real-time road network status and routing information from the other centers to aid in selecting the emergency vehicle(s) and routes, and works with other relevant centers to tailor traffic control to support emergency vehicle ingress and egress, implementation of special traffic restrictions and closures, evacuation traffic control plans, and other special strategies that adapt the transportation system to better meet the unique demands of an emergency. |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | 'ITS Roadway Equipment' represents the ITS equipment that is distributed on and along the roadway that monitors and controls traffic and monitors and manages the roadway. This physical object includes traffic detectors, environmental sensors, traffic signals, highway advisory radios, dynamic message signs, CCTV cameras and video image processing systems, grade crossing warning systems, and ramp metering systems. Lane management systems and barrier systems that control access to transportation infrastructure such as roadways, bridges and tunnels are also included. This object also provides environmental monitoring including sensors that measure road conditions, surface weather, and vehicle emissions. Work zone systems including work zone surveillance, traffic control, driver warning, and work crew safety systems are also included. |
| Maint and Constr Management Center | Center | The 'Maint and Constr Management Center' monitors and manages roadway infrastructure construction and maintenance activities. Representing both public agencies and private contractors that provide these functions, this physical object manages fleets of maintenance, construction, or special service vehicles (e.g., snow and ice control equipment). The physical object receives a wide range of status information from these vehicles and performs vehicle dispatch, routing, and resource management for the vehicle fleets and associated equipment. The physical object participates in incident response by deploying maintenance and construction resources to an incident scene, in coordination with other center physical objects. The physical object manages equipment at the roadside, including environmental sensors and automated systems that monitor and mitigate adverse road and surface weather conditions. It manages the repair and maintenance of both non-ITS and ITS equipment including the traffic controllers, detectors, dynamic message signs, signals, and other equipment associated with the roadway infrastructure. Weather information is collected and fused with other data sources and used to support advanced decision support systems. The physical object remotely monitors and manages ITS capabilities in work zones, gathering, storing, and disseminating work zone information to other systems. It manages traffic in the vicinity of the work zone and advises drivers of work zone status (either directly at the roadside or through an interface with the Transportation Information Center or Traffic Management Center physical objects.) Construction and maintenance activities are tracked and coordinated with other systems, improving the quality and accuracy of information available regarding closures and other roadway construction and maintenance activities. |
| Media | Center | 'Media' represents the information systems that provide traffic reports, travel conditions, and other transportation-related news services to the traveling public through radio, TV, and other media. Traffic and travel advisory information that are collected by ITS are provided to this object. It is also a source for traffic flow information, incident and special event information, and other events that may have implications for the transportation system. |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment | Field | Representing another set of ITS Roadway Equipment, 'Other ITS Roadway Equipment' supports 'field device' to 'field device' communication and coordination, and provides a source and destination for information that may be exchanged between ITS Roadway Equipment. The interface enables direct coordination between field equipment. Examples include the direct interface between sensors and other roadway devices (e.g., Dynamic Message Signs) and the direct interface between roadway devices (e.g., between a Signal System Master and Signal System Local equipment) or a connection between an arterial signal system master and a ramp meter controller. |
| Traffic Management Center | Center | The 'Traffic Management Center' monitors and controls traffic and the road network. It represents centers that manage a broad range of transportation facilities including freeway systems, rural and suburban highway systems, and urban and suburban traffic control systems. It communicates with ITS Roadway Equipment and Connected Vehicle Roadside Equipment (RSE) to monitor and manage traffic flow and monitor the condition of the roadway, surrounding environmental conditions, and field equipment status. It manages traffic and transportation resources to support allied agencies in responding to, and recovering from, incidents ranging from minor traffic incidents through major disasters. |
| Traffic Operations Personnel | Center | 'Traffic Operations Personnel' represents the people that operate a traffic management center. These personnel interact with traffic control systems, traffic surveillance systems, incident management systems, work zone management systems, and travel demand management systems. They provide operator data and command inputs to direct system operations to varying degrees depending on the type of system and the deployment scenario. |
| Transit Management Center | Center | The 'Transit Management Center' manages transit vehicle fleets and coordinates with other modes and transportation services. It provides operations, maintenance, customer information, planning and management functions for the transit property. It spans distinct central dispatch and garage management systems and supports the spectrum of fixed route, flexible route, paratransit services, transit rail, and bus rapid transit (BRT) service. The physical object's interfaces support communication between transit departments and with other operating entities such as emergency response services and traffic management systems. |
| Transportation Information Center | Center | The 'Transportation Information Center' collects, processes, stores, and disseminates transportation information to system operators and the traveling public. The physical object can play several different roles in an integrated ITS. In one role, the TIC provides a data collection, fusing, and repackaging function, collecting information from transportation system operators and redistributing this information to other system operators in the region and other TICs. In this information redistribution role, the TIC provides a bridge between the various transportation systems that produce the information and the other TICs and their subscribers that use the information. The second role of a TIC is focused on delivery of traveler information to subscribers and the public at large. Information provided includes basic advisories, traffic and road conditions, transit schedule information, yellow pages information, ride matching information, and parking information. The TIC is commonly implemented as a website or a web-based application service, but it represents any traveler information distribution service. |
Includes Functional Objects:
| Functional Object | Description | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | 'Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination' includes field elements that provide information to drivers, including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radios. | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | 'TMC Traffic Information Dissemination' disseminates traffic and road conditions, closure and detour information, incident information, driver advisories, and other traffic-related data to other centers, the media, and driver information systems. It monitors and controls driver information system field equipment including dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio, managing dissemination of driver information through these systems. | Traffic Management Center |
Includes Information Flows:
| Information Flow | Description |
|---|---|
| advisory radio coordination | The direct flow of information between field equipment. This includes information used to initialize, configure, and control roadside highway advisory radio including message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support local monitoring and management of these systems. |
| broadcast advisories | General broadcast advisories that are provided over wide-area wireless communications direct to the vehicle radio. These analog advisory messages may provide similar content to ITS broadcast information flows, but include no digital data component. Existing Highway-Advisory Radio (HAR) advisory messages are a prime example of this flow. |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information provided to the driver to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. |
| dynamic sign coordination | The direct flow of information between field equipment. This includes information used to initialize, configure, and control dynamic message signs. This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support local management of these devices. Current operating status of dynamic message signs is returned. |
| road network conditions | Current and forecasted traffic information, road and weather conditions, and other road network status. Either raw data, processed data, or some combination of both may be provided by this flow. Information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions (lane/shoulder use, weight restrictions, width restrictions, HOV requirements) in effect is included. |
| roadway advisory radio data | Information used to initialize, configure, and control roadside highway advisory radio. This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support remote management of these systems. |
| roadway advisory radio status | Current operating status of highway advisory radios. |
| roadway dynamic signage data | Information used to initialize, configure, and control dynamic message signs. This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support remote management of these devices. |
| roadway dynamic signage status | Current operating status of dynamic message signs. |
| traffic control information | Represents the flow of traffic control and status information between centers. This is reporting only, not actual control. This specifically includes the current state of any demand management strategies that have been implemented. |
| traffic image meta data | Meta data that describes traffic images. Traffic images (video) are in another flow. |
| traffic images | High fidelity, real-time traffic images suitable for surveillance monitoring by the operator or for use in machine vision applications. This flow includes the images. Meta data that describes the images is contained in another flow. |
| traffic information for media | Report of traffic conditions including traffic incident reports for public dissemination through the media. The reports may also include information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions in effect. |
| traffic operator data | Presentation of traffic operations data to the operator including traffic conditions, current operating status of field equipment, maintenance activity status, incident status, video images, security alerts, emergency response plan updates and other information. This data keeps the operator appraised of current road network status, provides feedback to the operator as traffic control actions are implemented, provides transportation security inputs, and supports review of historical data and preparation for future traffic operations activities. |
| traffic operator input | User input from traffic operations personnel including requests for information, configuration changes, commands to adjust current traffic control strategies (e.g., adjust signal timing plans, change DMS messages), and other traffic operations data entry. |
Goals and Objectives
Associated Planning Factors and Goals
| Planning Factor | Goal |
|---|---|
| A. Support the economic vitality of the metropolitan area, especially by enabling global competitiveness, productivity, and efficiency; | Improve freight network |
| B. Increase the safety of the transportation system for motorized and nonmotorized users; | Reduce fatalities and injuries |
| D. Increase the accessibility and mobility of people and for freight; | Reduce congestion |
| E. Protect and enhance the environment, promote energy conservation, improve the quality of life, and promote consistency between transportation improvements and State and local planned growth and economic development patterns; | Protect/Enhance the Environment |
| F. Enhance the integration and connectivity of the transportation system, across and between modes, for people and freight; | Enhance integration and connectivity |
| G. Promote efficient system management and operation; | Improve efficiency |
| I. Improve the resiliency and reliability of the transportation system and reduce or mitigate stormwater impacts of surface transportation; | Improve resiliency and reliability |
| J. Enhance travel and tourism. | Support travel and tourism |
Associated Objective Categories 
Associated Objectives and Performance Measures 

Needs and Requirements
| Need | Functional Object | Requirement | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information to drivers using roadside devices such as dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio. | Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | 01 | The field element shall include dynamic message signs for dissemination of traffic and other information to drivers, under center control; the DMS may be either those that display variable text messages, or those that have fixed format display(s) (e.g. vehicle restrictions, or lane open/close). |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | 01 | The center shall remotely control dynamic messages signs for dissemination of traffic and other information to drivers. | ||
| 02 | Traffic Operations need to be able to monitor roadside devices used to provide traffic and traveler information to drivers. | Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination | 02 | The field element shall include driver information systems that communicate directly from a center to the vehicle radio (such as Highway Advisory Radios) for dissemination of traffic and other information to drivers, under center control. |
| 03 | The field element shall provide operational status for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.) to the center. | |||
| 04 | The field element shall provide fault data for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.) to the center for repair. | |||
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | 03 | The center shall collect operational status for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.). | ||
| 04 | The center shall collect fault data for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.) for repair. | |||
| 03 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information, including images to the media. | TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | 07 | The center shall distribute traffic data to the media. |
| 08 | The center shall provide the capability for center personnel to control the nature of the data that is available to non-traffic operations centers and the media. | |||
| 10 | The center shall provide traffic information in both data stream and graphical display. | |||
| 04 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information, including images to traveler information, transit, maintenance and emergency centers. | TMC Traffic Information Dissemination | 06 | The center shall distribute traffic data to maintenance and construction centers, transit centers, emergency management centers, parking facilities, and traveler information providers. |
Security
In order to participate in this service package, each physical object should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Physical Object Security | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Object | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability | Security Class |
| Basic Vehicle | Not Applicable | Low | Low | Class 1 |
| Emergency Management Center | Low | Low | Moderate | Class 1 |
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Class 2 |
| Maint and Constr Management Center | Low | Low | Moderate | Class 1 |
| Media | Low | Low | Moderate | Class 1 |
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Class 2 |
| Traffic Management Center | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Class 2 |
| Transit Management Center | Low | Low | Moderate | Class 1 |
| Transportation Information Center | Low | Low | Moderate | Class 1 |
In order to participate in this service package, each information flow triple should meet or exceed the following security levels.
| Information Flow Security | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Destination | Information Flow | Confidentiality | Integrity | Availability |
| Basis | Basis | Basis | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Basic Vehicle | broadcast advisories | Not Applicable | Low | Low |
| By definition this is publicly broadcast data. | Advisories should be correct, but this is usually considered | There are probably a variety of mechanisms for receiving this information. If this is the only mechanism, may rate this MODERATE. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Driver | driver information | Not Applicable | High | Moderate |
| This data is sent to all drivers and is also directly observable, by design. | This is the primary signal trusted by the driver to decide whether to go through the intersection and what speed to go through the intersection at; if it's wrong, accidents could happen. | If the lights are out you have to get a policeman to direct traffic – expensive and inefficient and may cause a cascading effect due to lack of coordination with other intersections. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Other ITS Roadway Equipment | advisory radio coordination | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Any control flow has some confidentiality requirement, as observation of the flow may enable an attacker to analyze and learn how to assume control. MODERATE for most flows as the potential damage is likely contained, though anything that could have a significant safety impact may be assigned HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should have MODERATE integrity at minimum, just to guarantee that intended control messages are received. Incorrect, corrupted, intercepted and modified control messages can or will result in target field devices not behaving according to operator intent. The severity of this depends on the type of device, which is why some devices are set MODERATE and some HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flow availability is related to the criticality of being able to remotely control the device. For most devices, this is MODERATE. For purely passive devices with no incident relationship, this will be LOW. All devices should have default modes that enable them to operate without backhaul connectivity, so no device warrants a HIGH. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Other ITS Roadway Equipment | dynamic sign coordination | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Any control flow has some confidentiality requirement, as observation of the flow may enable an attacker to analyze and learn how to assume control. MODERATE for most flows as the potential damage is likely contained, though anything that could have a significant safety impact may be assigned HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should have MODERATE integrity at minimum, just to guarantee that intended control messages are received. Incorrect, corrupted, intercepted and modified control messages can or will result in target field devices not behaving according to operator intent. The severity of this depends on the type of device, which is why some devices are set MODERATE and some HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flow availability is related to the criticality of being able to remotely control the device. For most devices, this is MODERATE. For purely passive devices with no incident relationship, this will be LOW. All devices should have default modes that enable them to operate without backhaul connectivity, so no device warrants a HIGH. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Traffic Management Center | roadway advisory radio status | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Device status information should not be available, as those with criminal intent may use this information toward their own ends. | Data is intended to feed dissemination channels, either C-ITS messages or DMS or other channels, so it should generally be correct as it is distributed widely and any forgery or corrupted data will have widespread impact. | Occasional outages of this flow will delay dissemination of the data to travelers (the eventual end user) which could have significant impacts on travel, both safety and mobility impacts. | |||
| ITS Roadway Equipment | Traffic Management Center | roadway dynamic signage status | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Device status information should not be available, as those with criminal intent may use this information toward their own ends. | Data is intended to feed dissemination channels, either C-ITS messages or DMS or other channels, so it should generally be correct as it is distributed widely and any forgery or corrupted data will have widespread impact. | Failure of this flow affects traveler information dissemination, the importance of which varies with the data contained in the flow and the scenario. Could be LOW in many instances. | |||
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | advisory radio coordination | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Any control flow has some confidentiality requirement, as observation of the flow may enable an attacker to analyze and learn how to assume control. MODERATE for most flows as the potential damage is likely contained, though anything that could have a significant safety impact may be assigned HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should have MODERATE integrity at minimum, just to guarantee that intended control messages are received. Incorrect, corrupted, intercepted and modified control messages can or will result in target field devices not behaving according to operator intent. The severity of this depends on the type of device, which is why some devices are set MODERATE and some HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flow availability is related to the criticality of being able to remotely control the device. For most devices, this is MODERATE. For purely passive devices with no incident relationship, this will be LOW. All devices should have default modes that enable them to operate without backhaul connectivity, so no device warrants a HIGH. | |||
| Other ITS Roadway Equipment | ITS Roadway Equipment | dynamic sign coordination | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Any control flow has some confidentiality requirement, as observation of the flow may enable an attacker to analyze and learn how to assume control. MODERATE for most flows as the potential damage is likely contained, though anything that could have a significant safety impact may be assigned HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flows, even for seemingly innocent devices, should have MODERATE integrity at minimum, just to guarantee that intended control messages are received. Incorrect, corrupted, intercepted and modified control messages can or will result in target field devices not behaving according to operator intent. The severity of this depends on the type of device, which is why some devices are set MODERATE and some HIGH. | Since this directly impacts device control, we consider it the same as a control flow. Control flow availability is related to the criticality of being able to remotely control the device. For most devices, this is MODERATE. For purely passive devices with no incident relationship, this will be LOW. All devices should have default modes that enable them to operate without backhaul connectivity, so no device warrants a HIGH. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Emergency Management Center | road network conditions | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| No harm should come from seeing this data, as it is eventually intended for public consumption. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to corroborate the data in many instances. Thus MODERATE generally. | Depends on the application; if mobility decisions that affect large numbers of travelers are made based on this data, then it is MODERATE. In more modest circumstances, it may be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Emergency Management Center | traffic image meta data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to function without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Emergency Management Center | traffic images | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While availability of imagery is useful for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally, though it could be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | roadway advisory radio data | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Device control information should not be available, as those with criminal intent may use this information toward their own ends. | Data is intended to feed dissemination channels, either C-ITS messages or DMS or other channels, so it should generally be correct as it is distributed widely and any forgery or corrupted data will have widespread impact. | Occasional outages of this flow will delay dissemination of the data to travelers (the eventual end user) which could have significant impacts on travel, both safety and mobility impacts. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | ITS Roadway Equipment | roadway dynamic signage data | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Device control information should not be available, as those with criminal intent may use this information toward their own ends. | Data is intended to feed dissemination channels, either C-ITS messages or DMS or other channels, so it should generally be correct as it is distributed widely and any forgery or corrupted data will have widespread impact. | Occasional outages of this flow will delay dissemination of the data to travelers (the eventual end user) which could have significant impacts on travel, both safety and mobility impacts. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Maint and Constr Management Center | road network conditions | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| No harm should come from seeing this data, as it is eventually intended for public consumption. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to corroborate the data in many instances. Thus MODERATE generally. | Depends on the application; if mobility decisions that affect large numbers of travelers are made based on this data, then it is MODERATE. In more modest circumstances, it may be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Maint and Constr Management Center | traffic image meta data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to function without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Maint and Constr Management Center | traffic images | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While availability of imagery is useful for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally, though it could be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Media | traffic image meta data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to function without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Media | traffic images | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While availability of imagery is useful for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally, though it could be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Media | traffic information for media | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| This information is intended for distribution to all members of the traveling public. | Traffic information needs to be accurate, as it will be used by travelers to make decisions regarding their travel. Inaccurate or corrupted data could reduce overall mobility and certainly impact individual drivers. | There should be other means for getting this information, but as this is the 'source flow' for a wide area broadcast with a huge potential distribution, the breadth of the impact covers all travelers. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Traffic Operations Personnel | traffic operator data | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
| Backoffice operations flows should have minimal protection from casual viewing, as otherwise imposters could gain illicit control or information that should not be generally available. | Information presented to backoffice system operators must be consistent or the operator may perform actions that are not appropriate to the real situation. | The backoffice system operator should have access to system operation. If this interface is down then control is effectively lost, as without feedback from the system the operator has no way of knowing what is the correct action to take. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transit Management Center | road network conditions | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| No harm should come from seeing this data, as it is eventually intended for public consumption. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to corroborate the data in many instances. Thus MODERATE generally. | Depends on the application; if mobility decisions that affect large numbers of travelers are made based on this data, then it is MODERATE. In more modest circumstances, it may be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transit Management Center | traffic image meta data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to function without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transit Management Center | traffic images | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While availability of imagery is useful for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally, though it could be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transportation Information Center | road network conditions | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| No harm should come from seeing this data, as it is eventually intended for public consumption. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to corroborate the data in many instances. Thus MODERATE generally. | Depends on the application; if mobility decisions that affect large numbers of travelers are made based on this data, then it is MODERATE. In more modest circumstances, it may be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transportation Information Center | traffic control information | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Generally, center-originating flows destined for a TIC don't contain any personal or confidential information, and are eventually intended for some kind of public consumption. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transportation Information Center | traffic image meta data | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Traffic image data is generally intended for public consumption, and in any event is already video captured in the public arena, so this must be LOW. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to function without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | |||
| Traffic Management Center | Transportation Information Center | traffic images | Low | Moderate | Moderate |
| Intended for widespread and public distribution, so no reason to conceal. | While accuracy of this data is important for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally. | While availability of imagery is useful for decision making purposes, applications should be able to cfunction without it. Thus MODERATE generally, though it could be LOW. | |||
| Traffic Operations Personnel | Traffic Management Center | traffic operator input | Moderate | High | High |
| Backoffice operations flows should have minimal protection from casual viewing, as otherwise imposters could gain illicit control or information that should not be generally available. | Backoffice operations flows should generally be correct and available as these are the primary interface between operators and system. | Backoffice operations flows should generally be correct and available as these are the primary interface between operators and system. | |||
Standards
The following table lists the standards associated with physical objects in this service package. For standards related to interfaces, see the specific information flow triple pages.
| Name | Title | Physical Object |
|---|---|---|
| ITE 5201 ATC | Advanced Transportation Controller | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| ITE 5202 ATC Model 2070 | Model 2070 Controller Standard | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| ITE 5301 ATC ITS Cabinet | Intelligent Transportation System Standard Specification for Roadside Cabinets | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| ITE 5401 ATC API | Application Programming Interface Standard for the Advanced Transportation Controller | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| NEMA TS 8 Cyber and Physical Security | Cyber and Physical Security for Intelligent Transportation Systems | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| Traffic Management Center | ||
| NEMA TS2 Traffic Controller Assemblies | Traffic Controller Assemblies with NTCIP Requirements | ITS Roadway Equipment |
| NEMA TS4 Hardware Standards for DMS | Hardware Standards for Dynamic Message Signs (DMS) With NTCIP Requirements | ITS Roadway Equipment |
System Requirements
| System Requirement | Need | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | The system shall remotely control dynamic messages signs for dissemination of traffic and other information to drivers. | 01 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information to drivers using roadside devices such as dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio. |
| 002 | The system shall collect operational status for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.). | 02 | Traffic Operations need to be able to monitor roadside devices used to provide traffic and traveler information to drivers. |
| 003 | The system shall collect fault data for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.) for repair. | 02 | Traffic Operations need to be able to monitor roadside devices used to provide traffic and traveler information to drivers. |
| 004 | The system shall distribute traffic data to maintenance and construction centers, transit centers, emergency management centers, parking facilities, and traveler information providers. | 04 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information, including images to traveler information, transit, maintenance and emergency centers. |
| 005 | The system shall distribute traffic data to the media. | 03 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information, including images to the media. |
| 006 | The system shall provide the capability for center personnel to control the nature of the data that is available to non-traffic operations centers and the media. | 03 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information, including images to the media. |
| 007 | The system shall provide traffic information in both data stream and graphical display. | 03 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information, including images to the media. |
| 008 | The system shall include dynamic message signs for dissemination of traffic and other information to drivers, under center control; the DMS may be either those that display variable text messages, or those that have fixed format display(s) (e.g. vehicle restrictions, or lane open/close). | 01 | Traffic Operations need to be able to provide traffic and incident information to drivers using roadside devices such as dynamic message signs and highway advisory radio. |
| 009 | The system shall include driver information systems that communicate directly from a center to the vehicle radio (such as Highway Advisory Radios) for dissemination of traffic and other information to drivers, under center control. | 02 | Traffic Operations need to be able to monitor roadside devices used to provide traffic and traveler information to drivers. |
| 010 | The system shall provide operational status for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.) to the center. | 02 | Traffic Operations need to be able to monitor roadside devices used to provide traffic and traveler information to drivers. |
| 011 | The system shall provide fault data for the driver information systems equipment (DMS, HAR, etc.) to the center for repair. | 02 | Traffic Operations need to be able to monitor roadside devices used to provide traffic and traveler information to drivers. |
Implementations


TM06.1 Dynamic Message Signs Implementation
Use dynamic message signs (DMS) to provide information to passing vehicles.
Dynamic Message Signs Implementation Flows
| Information Flow | Description | Inclusion Status |
|---|---|---|
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information provided to the driver to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. | Fundamental |
| dynamic sign coordination | The direct flow of information between field equipment. This includes information used to initialize, configure, and control dynamic message signs. This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support local management of these devices. Current operating status of dynamic message signs is returned. | Optional |
| road network conditions | Current and forecasted traffic information, road and weather conditions, and other road network status. Either raw data, processed data, or some combination of both may be provided by this flow. Information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions (lane/shoulder use, weight restrictions, width restrictions, HOV requirements) in effect is included. | Optional |
| roadway dynamic signage data | Information used to initialize, configure, and control dynamic message signs. This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support remote management of these devices. | Fundamental |
| roadway dynamic signage status | Current operating status of dynamic message signs. | Fundamental |
| traffic control information | Represents the flow of traffic control and status information between centers. This is reporting only, not actual control. This specifically includes the current state of any demand management strategies that have been implemented. | Optional |
| traffic image meta data | Meta data that describes traffic images. Traffic images (video) are in another flow. | Optional |
| traffic images | High fidelity, real-time traffic images suitable for surveillance monitoring by the operator or for use in machine vision applications. This flow includes the images. Meta data that describes the images is contained in another flow. | Optional |
| traffic information for media | Report of traffic conditions including traffic incident reports for public dissemination through the media. The reports may also include information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions in effect. | Optional |
| traffic operator data | Presentation of traffic operations data to the operator including traffic conditions, current operating status of field equipment, maintenance activity status, incident status, video images, security alerts, emergency response plan updates and other information. This data keeps the operator appraised of current road network status, provides feedback to the operator as traffic control actions are implemented, provides transportation security inputs, and supports review of historical data and preparation for future traffic operations activities. | Optional |
| traffic operator input | User input from traffic operations personnel including requests for information, configuration changes, commands to adjust current traffic control strategies (e.g., adjust signal timing plans, change DMS messages), and other traffic operations data entry. | Optional |
Dynamic Message Signs Implementation Functional Objects
| Functional Object |
|---|
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination |
Back to Implementation List
TM06.2 Advisory Radio Implementation
Use advisory radios (e.g., Highway Advisory Radio (HAR)) to provide information to passing vehicles.
Advisory Radio Implementation Flows
| Information Flow | Description | Inclusion Status |
|---|---|---|
| advisory radio coordination | The direct flow of information between field equipment. This includes information used to initialize, configure, and control roadside highway advisory radio including message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support local monitoring and management of these systems. | Optional |
| broadcast advisories | General broadcast advisories that are provided over wide-area wireless communications direct to the vehicle radio. These analog advisory messages may provide similar content to ITS broadcast information flows, but include no digital data component. Existing Highway-Advisory Radio (HAR) advisory messages are a prime example of this flow. | Fundamental |
| driver information | Regulatory, warning, guidance, and other information provided to the driver to support safe and efficient vehicle operation. | Fundamental |
| road network conditions | Current and forecasted traffic information, road and weather conditions, and other road network status. Either raw data, processed data, or some combination of both may be provided by this flow. Information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions (lane/shoulder use, weight restrictions, width restrictions, HOV requirements) in effect is included. | Optional |
| roadway advisory radio data | Information used to initialize, configure, and control roadside highway advisory radio. This flow can provide message content and delivery attributes, local message store maintenance requests, control mode commands, status queries, and all other commands and associated parameters that support remote management of these systems. | Fundamental |
| roadway advisory radio status | Current operating status of highway advisory radios. | Fundamental |
| traffic control information | Represents the flow of traffic control and status information between centers. This is reporting only, not actual control. This specifically includes the current state of any demand management strategies that have been implemented. | Optional |
| traffic image meta data | Meta data that describes traffic images. Traffic images (video) are in another flow. | Optional |
| traffic images | High fidelity, real-time traffic images suitable for surveillance monitoring by the operator or for use in machine vision applications. This flow includes the images. Meta data that describes the images is contained in another flow. | Optional |
| traffic information for media | Report of traffic conditions including traffic incident reports for public dissemination through the media. The reports may also include information on diversions and alternate routes, closures, and special traffic restrictions in effect. | Optional |
| traffic operator data | Presentation of traffic operations data to the operator including traffic conditions, current operating status of field equipment, maintenance activity status, incident status, video images, security alerts, emergency response plan updates and other information. This data keeps the operator appraised of current road network status, provides feedback to the operator as traffic control actions are implemented, provides transportation security inputs, and supports review of historical data and preparation for future traffic operations activities. | Optional |
| traffic operator input | User input from traffic operations personnel including requests for information, configuration changes, commands to adjust current traffic control strategies (e.g., adjust signal timing plans, change DMS messages), and other traffic operations data entry. | Optional |
Advisory Radio Implementation Functional Objects
| Functional Object |
|---|
| Roadway Traffic Information Dissemination |
| TMC Traffic Information Dissemination |
Back to Implementation List
